* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelle
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
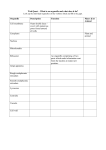
Catalyst #2: November 12, 2013 (4 minutes) 1. What type of cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles? 2. What important structure do prokaryotic cells not have? 3. The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle. You discover a cell with a Golgi apparatus. What type of cell is it? 4. What type of organism– prokaryote or eukaryote is pictured below? Agenda • • • • Catalyst (5 minutes) Organelle Notes (10 minutes) Organelle Whiteboard Activity (10 minutes) Labeling and Review Questions (10 minutes) • Exit Ticket (3 minutes) • Homework: – Quiz tomorrow (Chapter 7; Section 1) – Read section 7.3 in your book Agenda: Honors • • • • Catalyst (5 minutes) Organelle Notes (10 minutes) Organelle Jigsaw ( 15 minutes) Review questions (Remainder) • Homework: – Quiz tomorrow (Chapter 7; Section 1) – Read section 7.3 in your book – Honors Project Announcements • Grade slips/Mastery • Discovery letters • Dojo Unit 5: Guiding Questions • What are all living organisms made up of? • What does each part of the cell do? • What different types of cells exist and how are they different? Today’s Objectives • SWBAT describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, and lysosomes • • SWBAT identify and label the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondria Cellular Organelles Biology Unit 5 Lesson 4 Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Review questions • On whiteboards • Expectations/Rules Question • Who discovered the cell in 1665? • Answer: Robert Hooke Question • What three features do all cells have? • Answer: Cell membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material Question • What is the name of the outer layer of the cell that consists of two layers of lipids? • Answer: The cell membrane Question • What two types of genetic material can be found in cells? • Answer: DNA and RNA Question • What type of cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles? • Answer: Eukaryotic Question • The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle that packages the proteins produced in cells. In what type of cells is the Golgi apparatus found? • Answer: Eukaryotic Question • What type of cell is pictured to the right? • How do you know? • Answer: Prokaryotic (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Question • What type of cell is pictured to the left? • How do you know? • Answer: Eukaryotic (it has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Question • Each Chlamydia bacterium is a unicellular organism also. Is Chlamydia a prokaryote or eukaryote? • Answer: Prokaryote Question • Is a mushroom a prokaryote or eukaryote? • How do you know? • Answer: Eukaryote, because it is multi-cellular Review: Cells • All organisms are made up of one or more cells • All cells have three features: – Cell membrane – Cytoplasm – Genetic material Review: Prokayotic vs. Eukaryotic • PROKARYOTIC – No nucleus – No membranebound organelles – Only unicellular organisms – Example: Bacteria • EUKARYOTIC – Have a nucleus – Have membranebound organelles – Can form multicellular organisms – Examples: All cells in plants, animals, humans Honors: Specialized Form, Function, and Size • Because a major theme in Biology is function dictates form, not all cells look alike. – Examples: Nerve cells, Fat cells (Adipose cells), White blood cells Honors: Specialized Form, Function, and Size • The human body consists of two hundred cell types, each with a different function and different form. • Even though cell have different functions, they all have the same organelles. Organelles • Every structure in the cell has a specific function that is important to the cell • Organelles are small structures inside of the cell that have specific functions • Only eukaryotic cells have membranebound organelles Factory Analogy • To help us remember all the organelles and their functions, we will make comparisons to jobs/roles in a factory/business. Cell Membrane • One structure that all cells have is a cell membrane • Organelle: Cell Membrane – Outer layer of lipids around the cell • Function: Controls what enters and leaves the cell. It is “selectively permeable” – Selects what goes through and what doesn’t – Factory Role: Security Guard Cell Membrane Membrane-Bound Organelles • The next three structures are membranebound organelles • In what type of cell are they located? – Only eukaryotic cells Nucleus • One key organelle found only in eukaryotic cells is the nucleus • Organelle: Nucleus – Large round structure with dark center (nucleolus) • Function: Stores genetic material and controls the activities of the cell – “Brain” or “command center” of the cell – Factory Role: The Boss/CEO Nucleus: Honors • One key organelle found only in eukaryotic cells is the nucleus • Organelle: Nucleus – Large round structure with dark center (nucleolus) • Function: Stores genetic material and controls the activities of the cell • Genetic material contained as chromosomes • Surrounded by a protective nuclear envelope that contains pores and is semipermeable like the cell membrane – “Brain” or “command center” of the cell – Factory Role: The Boss/CEO Nucleus Mitochondria • Another key organelle found in eukaryotic organelles is the mitochondrion • Organelle: Mitochondria – Oval structure with inner folds • Function: Produce energy known as ATP for the cell – “Powerhouse” of the cell – Factory Role: Power source Mitochondria: Honors • Another key organelle found in eukaryotic organelles is the mitochondrion • Organelle: Mitochondria – Oval structure with inner folds • Function: Produce energy known as ATP for the cell through the process of cellular respiration • Mitochondria contain their own DNA that is used to compensate for any defects – “Powerhouse” of the cell – An average cell can contain 2,500 of them – Factory Role: Power source Mitochondrion Lysosomes • Lysosomes are another membranebound organelle • Structure: Lysosomes – Smaller round structures • Function: Destroy waste and digest macromolecules inside the cell • Factory Role: Janitors Lysosomes Summary • The eukaryotic cell has many structures with many important functions – Cell membrane– selects what enters and leaves the cell – Nucleus– stores genetic material and controls cellular activities – Mitochondria– produce energy for the cell in the form of ATP – Lysosomes– destroy waste and digest macromolecules Instructions: Regular • Match the organelle name + function to the large cell on the board; copy these labels/functions down onto the cell on your notes. Instructions: Honors • Divided into groups • Your group will be assigned an organelle that we discussed today • You will have ONE MINUTE to find an object in our classroom that exemplifies the FUNCTION of the organelle. • Fill out your group slip. • As each group presents, fill out your evaluation table. Exit Ticket • Answer the questions below without using your notes: 1. What is the function of the cell membrane? 2. What organelle stores genetic material in the eukaryotic cell? 3. What is the function of mitochondria? Catalyst: November 13, 2013 • You need a sheet of paper numbered 1 – 10 for our Cell quiz. Agenda • Catalyst: 10 minutes • Cellular Organelles: Part 2: 15 minutes • Review Questions + Grudgeball: Remainder – FINISH CELLULAR ORGANELLES WORKSHEET – Read section 7.3 in your book Agenda: Honors • • • • Catalyst: 10 minutes Cellular Organelles: Part 2: 15 minutes Prepare Overton bacteria cultures: 15 minutes Review Questions: Remainder – FINISH CELLULAR ORGANELLES WORKSHEET – Read section 7.3 in your book – Honors Project Announcements • Dojo review • Mastery slips • Discovery letters Review • What is the function of the cell membrane? – Controls what enters and leaves the cell • What is the function of the nucleus? – Controls the activities of the cell • What do mitochondria do? – Produce energy (ATP) for the cell • What do lysosomes do? – Destroy waste inside the cell Ribosomes • Ribosomes are important organelles that are not membrane-bound • Organelle: Ribosomes – Tiny, round structures • Function: Synthesize (produce) proteins needed by the cell – Location of protein synthesis – Can be found free in cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum – Factory Role: Production Machines Ribosomes: Honors • Ribosomes are important organelles that are not membrane-bound • Organelle: Ribosomes – Tiny, round structures • Function: Synthesize (produce) proteins needed by the cell – Location of protein synthesis – Can be found free in cytoplasm (used for protein production) or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (used for export) – Factory Role: Production Machines Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of folded membranes that surrounds the nucleus and spreads throughout the cell • Two types: – Rough ER– covered by ribosomes – Smooth ER– not covered by ribosomes Rough ER • The rough endoplasmic reticulum is only in eukaryotic cells • Organelle: Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – Series of folded membranes covered by ribosomes • Function: Transports proteins throughout the cell – Roads for proteins – Factory Role: Assembly line Rough ER Smooth ER • The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is only in the eukaryotic cell • Organelle: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – Not covered by ribosomes • Function: Synthesizes (produces) lipids for the cell • Factory Role: Assembly line Smooth ER: Honors • The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is only in the eukaryotic cell • Organelle: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – Not covered by ribosomes • Function: Synthesizes (produces) lipids for the cell • Detoxifies drugs and poisons from the body Smooth ER Golgi Apparatus • The Golgi apparatus is another membranebound organelle • Organelle: Golgi apparatus – Stack of membranes (What does it look like?!) • Function: Sorts and packages proteins and lipids to be shipped out of the cell • Factory Role: Delivery Trucks Golgi Apparatus Peroxisomes • Organelle: Peroxisomes • Function: Detoxification of cellular waste • Factory role: Hazardous materials cleanup Vacuoles • Organelle: Vacuole • Function: Stores water; breakdown; chemical storage • Factory role: Storage closets Summary • Many of the organelles have functions involving proteins and also lipids – Ribosomes synthesize proteins – The rough ER then transports the proteins throughout the cell – The smooth ER synthesize lipids – The Golgi apparatus packages the proteins and lipids to be shipped out of the cell Instructions: Regular • Complete the Cellular Organelles Worksheet • We will play Grudgeball to review the questions after ten minutes. • Any questions not finished will be due for homework. Instructions: Honors • Prepare Overton Bacteria Cultures • Overview • Materials • Procedure Exit Ticket: Day 2 1. What is the function of the ribosomes? 2. What does the rough ER do with proteins? 3. What part of the cell synthesizes (produces) lipids? 4. What does the Golgi apparatus do?