* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study/Review * Nervous System Part 2 * CNS and PNS
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
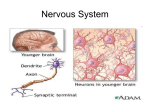
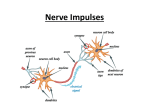
Biology 102 Nervous System: Neurons, Nerve Impulse, and Neurotransmitters Study Guide and Review Match the following terms with statements below. Make up your own statement for terms that are not used. A. B. C. D. E. Dendrites Axon Sensory neurons Interneurons Motor neurons F. Astrocyte G. Oligodendrocyte H. Schwann cells I. Microglia J. Effector K. Neuroglia L. Myelin sheath _____ General term for cells that nourish and support neurons __E___ Gland or muscle cell _____ Cells that eat foreign material (phagocytic cells) __A___ Short extensions that carry impulses to the cell body of the neuron _____ Neurons in the CNS only _____ Protective and insulating “jelly roll” on axons of PNS and CNS __B__ Long extension that carries impulses away from the cell body __C___ Take nerve impulses from a sensory receptor to the CNS _____ Cells that provide nutrients and hormones for neurons _____ Take impulses from CNS to effectors _____ Cells that make myelin sheath in the PNS Fill in the blank: 1. Chemicals stored at the ends of axons and responsible for transmission of an impulse across the synaptic cleft are called ____________________________ 2. These cells make myelin on axons of the CNS: _______________________ 3. _________________________ are gaps in the myelin sheath 4. A change in ion/charge distribution across the axon membrane is called ___________________________ 5. ___________________is a region between an axon terminal and a dendrite or cell body of another neuron 6. The name of an autoimmune demyelination disease characterized by antibodies to myelin is _________________________________ Nerve Impulses – Give a brief description of what happens when a nerve is resting and when there is a nerve impulse by filling in the table below. Include the following information: o Voltage (positive or negative) – as would be measured by a volt meter o Charge distribution – inside and outside of the axon membrane o What are the conditions that result in the stated charge distribution/voltage with respect to sodium/potassium ions Condition Voltage (+ or -) Charge outside axon membrane Charge inside axon membrane No impulse (resting) ‘polarization’ Nerve impulse Depolarization Nerve impulse Repolarization No impulse (resting) ‘polarization’ Compare myelinated vs. non-myelinated axons: a) Speed of the impulse b) What is the role of myelination? Why? How? Synapses Draw a synapse and label major parts: Word Bank: presynaptic membrane, synaptic cleft (gap), postsynaptic membrane, neurotransmitter in vesicles, receptors How does the nerve impulse get across the gap? What is the role of calcium at the synapse? Tell what happens (step by step) at a synapse. What is the difference between excitation and inhibition? Practice with multiple choice: 1. Which of the following is not a neurotransmitter? a. Serotonin b. Norepinephrine c. Acetylcholine d. Dopamine 2. Antidepressants like Prozac act by a. Looking like a receptor for neurotransmitters b. Causing excitation of ‘happy’ neurons c. Preventing reabsorption of neurotransmitters d. Preventing degradation of neurotransmitters 3. What type of neuron lies completely in the CNS? a. Motor b. Interneurons c. Sensory 4. Neuroglial cells forming myelin sheaths in the PNS are a. Oligodendrocytes b. Ganglionic cells c. Schwann cells d. Microglia 5. Which of these correctly describes the distribution of ions on either side of an axon when it is not conducting a nerve impulse? a. More sodium ions outside and more potassium ions inside b. More potassium ions outside and less sodium ions inside c. Charged proteins outside and sodium and potassium ions inside d. Sodium and potassium ions inside and water only inside 6. When the action potential begins, sodium gates open, allowing sodium ions to cross the membrane. Now the polarity changes to a. Negative outside and positive inside b. Positive outside and negative inside c. Neutral outside and positive inside d. Neutral inside and positive outside 7. Repolarization of an axon during an action potential is produced by a. Inward diffusion of sodium ions b. Outward diffusion of potassium ions c. Inward active transport of sodium ions d. Active extrusion of potassium ions 8. Transmission of the nerve impulse across a synapse is accomplished by the a. Movement of sodium and potassium ions b. Release of a neurotransmitter by a dendrite c. Release of a neurotransmitter by an axon d. Release of a neurotransmitter by a cell body 9. Synaptic vesicles are a. At the ends of dendrites and axons b. At the ends of axons only c. Along the length of all long fibers d. All of these are correct 10. What mechanism is responsible for maintaining the unequal distribution of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane of an axon? a. Nodes of ranvier c. Sodium-potassium pumps b. Gated ion channels d. Osmosis 11. What term is used to describe how an action potential ‘jumps’ down a myelinated axon? a. Saltatory conduction c. Osmosis b. Schwann cell conduction d. Refractory period 12. What ion is critical for the release of neurotransmitters at a synapse? a. H+ b. Na+ c. K+ d. Ca++ 13. When an action potential begins, what causes the depolarization of the axon? a. A rush of Na+ out of the axon c. A rush of Na+ ions into the axon b. A rush of K+ ions out of the axon d. A rush of K+ ions into the axon










![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)