* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System Overview
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
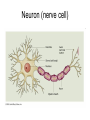
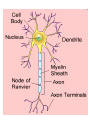
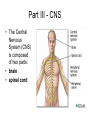
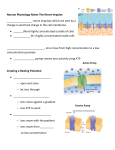
Nervous System Neuron (nerve cell) Structure Function Cell Body Central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell. where most protein synthesis occurs. Dendrites cellular extensions where the majority of input to the neuron occurs. Axon cable-like projection carries nerve signals. Extensive branching, enables communication with many target cells. Schwann Cell / Myelin Sheath Schwann cells wrap around the axon to form the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath insulates the axon and speeds up nerve impulses Axon Terminals contains synapses, where neurotransmitter chemicals are released in order to communicate with target neurons. Part II • 1. Electrical signals that are transmitted by the neuron are called neural signals. • 2. The junction between 2 neurons is called the Synapse. • 3. The transmitting cell is called the sensory neuron. • 4. The receiving cell is called the motor neuron. • 5. Membrane potential is: the charge inside of a neuron, relative to the outside while resting or unstimulated. Part II • 6. In a resting nerve cell, the outside of the cell membrane is electrically positive with respect to the inside of the cell. • 7. In a resting nerve cell, the concentration of sodium ions is higher outside the cell membrane than within the cell. • 8. In the are of the nerve impulse, the cell membrane becomes permeable to sodium ions. • 9. In the area of the nerve impulse, the outside of the cell membrane becomes electrically negative with respect to the inside. Part II • 10. How are sodium ions moved out of the neuron? There is a pump that uses energy to move three sodium ions out of the neuron for every two potassium ions it puts in. • 11. What role do Potassium ions play in action potential? At rest, potassium ions (K+) can cross through the membrane easily. Also at rest, chloride ions (Cl-)and sodium ions (Na+) have a more difficult time crossing. Potassium ions help to pump sodium into the cell to change the charge. Part II • 12. What is the refractory period? It is the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state Part III - CNS • The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of two parts: • brain • spinal cord Part IV - PNS • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of: • somatic nervous system (voluntary) • autonomic nervous system (involuntary)