* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Adult neurogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Hippocampus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor wikipedia , lookup
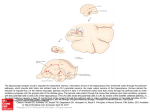
Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells and dentate gyrus granule cells—are connected by the mossy fiber (mf) and Schaffer collateral (SC) pathways. Chronic stress decreases the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus, which in turn may contribute to the atrophy of CA3 neurons and their increased vulnerability to a variety of neuronal insults. Chronic elevation of glucocorticoid levels is also known to decrease the survival of these neurons. In contrast, antidepressant treatments increase the expression of BDNF, as well as that of the BDNF receptor, TrkB, and prevent the downregulation of BDNF elicited Source: Mood and Emotion, Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience, 3e by stress. Such activity may increase the dendritic arborizations and survival of the neurons, or help repair or protect the neurons from further damage. Citation: Nestler EJ, Hyman SE, Holtzman DM, Malenka RC. Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience, 3e; 2015 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 04, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved