* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
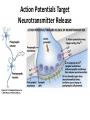
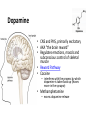
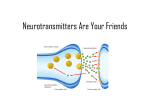
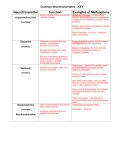
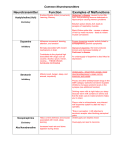
The Nervous System-Part II Neurotransmitters Action Potentials Target Neurotransmitter Release Neurotransmitters • • • • Found in CNS and PNS Over 100 in the body Can be excitatory or inhibitory Once released neurotransmitters will be decomposed by enzymes or up-taken by transporters in the pre-synaptic membrane • Classified as: acetylcholine, monoamines, amino acids, neuropeptides and gases Excitatory vs. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters Excitatory neurotransmitters • Increase postsynaptic membrane permeability to Na+ • Threshold is reached for message to be sent Inhibitory neurotransmitters • Decrease permeability to Na+ • Decreases chance nerve impulse will occur. Acetylcholine (ACh) • First neurotransmitter discovered (1921) • Excitatory in the CNS and PNS • Skeletal muscle neuromuscular junctions & synapses between the brain and spinal cord • Message causes muscles to contract or continues impulses • Nicotine inactivates ACH receptors and causes brain to create more receptors Glutamate • Found in the CNS, generally excitatory – helps send messages in the brain • Involved in learning and memory • Alcohol inhibits glutamate receptor function • Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is a food additive that stimulates glutamate receptors in the taste buds! Serotonin • Found in the CNS, primarily inhibitory • Responsible for sleep, mood and temperature regulation • Antidepressants (Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, etc) work by allowing serotonin to accumulate in the synapse, – “SSRI’s” or Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors – feel more content • LSD mimics serotonin, and MDMA releases excess serotonin Dopamine • CNS and PNS, primarily excitatory • AKA “the brain reward” • Regulates emotions, moods and subconscious control of skeletal muscle • Reward Pathway • Cocaine – interferes with the process by which dopamine is taken back up (leaves more in the synapse) • Methamphetamine – excess dopamine release Dopamine - cont’d • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors GABA • CNS, generally inhibitory • Found in the brain • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed Norepinephrine • CNS and PNS, primarily excitatory • Found in the brain, promotes feeling good, low levels linked to depression • Alertness, regulation of moods • In the PNS may excite or inhibit based on receptors Endorphins • Primarily inhibitory, cause release of substance P • Flood the synaptic cleft during pain or stress – Usually inhibit neurons from firing, causing an analgesic effect – At lower levels can excite the next neuron • Reduces pain and makes one feel good • “Opiates” (heroin, codeine, morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, etc) – bind to endorphin receptors and mimic endorphins Anandamide • Involved in working memory, regulation of feeding behavior, generation of motivation and pleasure • Anandamide receptors are called cannabinoid receptors – A lot of cannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus (short term memory), cerebellum (coordination) and basal ganglia (unconcious muscle movement) of brain • THC (found in marijuana) mimics anandamides and binds to cannabinoid receptors • How Marijuana Works in the Brain