* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bicameralism (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Bird vocalization wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Animal echolocation wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
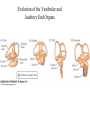
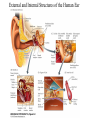
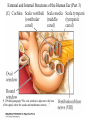
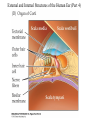
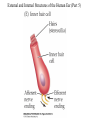
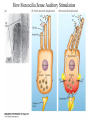
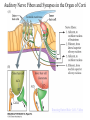
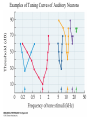
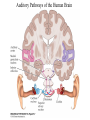
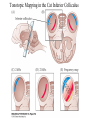
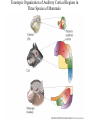
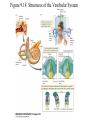
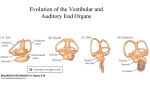
Evolution of the Vestibular and Auditory End Organs External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 3) P. 259 third paragraph “The oval window is adjacent to the base of the spiral, where the canals and membranes narrow; …” External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 4) External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 5) How Stereocilia Sense Auditory Stimulation Auditory Nerve Fibers and Synapses in the Organ of Corti Dancing Outer Hair Cell - Video Basilar Membrane Movement for Sounds of Different Frequencies Basilar Membrane is five times wider at the apex Auditory neurons have tonotopic organization. Can hear sounds in a range from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter12.html Examples of Tuning Curves of Auditory Neurons Auditory Pathways of the Human Brain Tonotopic Mapping in the Cat Inferior Colliculus Tonotopic Organization of Auditory Cortical Regions in Three Species of Mammals Long-Term Retention of a Trained Shift in Tuning of an Auditory Receptive Field Auditory-Object Perception • Auditory object is the fundamental perceptual unit in hearing • Similar to visual objects although made up of spectrotemporal regularities • Auditory scene contains numerous acoustic stimuli • Activity in auditory circuits represents auditory objects • Neural responses become correlated with a listener's perceptual reports at the level of the cortex Figure 9.18 Structures of the Vestibular System Nerve Fibers from the Vestibular Portion of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII) Synapse in the Brainstem • Nerve fibers from vestibular receptors synapse in • the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem • some fibers go directly to the cerebellum. • The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) allows you to gaze at a fixed point while the head moves. The Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex