* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ascending Tracts - Bell`s Palsy
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
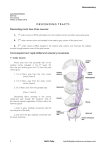
Neuroanatomy Luka Tomšič Ahčin Bell’s Palsy Neuroanatomy Written: 2 October 2010 ASCENDING TRACTS They are located in the white matter and conduct afferent information (may or may not reach consciousness). There are two types of information: 1. Exteroceptive : originates from outside the body (pain, temperature and touch) 2. Proprioceptive : originates from inside the body (from muscles and joints) Normally there are three neurons in an ascending pathway: 1. 1st order neuron: cell body is in the posterior root ganglion 2. ! 2nd order neuron: decussates (crosses to the opposite side) and ascends to a higher level of the CNS 3. 3rd neuron: located in the thalamus and passes to a sensory region of the cortex Pain and temperature pathway: lateral spinothalmic tract 1st order neuron Peripheral process extends to skin or other tissues and ends as free nerve endings (receptors). Cell body is situated in the posterior root ganglion. Central process extends into the posterior grey column and synapses with the 2nd order neuron. 2nd order neuron The axon crosses obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior grey and white commissures within one spinal segment of the cord. It ascends in the contr alater al white column as the later al spinothalamic tract (LSTT). As the LSTT ascends through the spinal cord new fibers are added to the anteromedial aspect of the tract (sacral fibers are lateral and cervical fibers are medial). The fibers carrying pain are situated anterior to those conducting temperature. As the LSTT ascends through the medulla oblongata, it's joined by the anterior spinothalamic tract and the spinotectal tract and forms the spinal lemniscus. Spinal lemniscus ascends through the pons and the mid brain. Fibers of the LSTT end by synapsing with the 3rd 1! Bell’s Palsy http://bellspalsycranialnerves.wordpress.com/ Neuroanatomy order neurons in the ventral posterolateral nucleus temperature sensations are appreciated). of the thalamus (here crude pain and 3rd order neuron Axons pass through the posterior limb of the internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the somatosensory area in the post central gyrus of the cerebral cortex. From here information is transmitted to other regions of the cerebral cortex to be used by motor areas. The role of the cerebral cortex is interpreting the quality of the sensory information at the level of the consciousness. Light (crude) touch and pressure pathway: anterior spinothalamic tract (ASTT) 1st order neuron It is similar to the pain and temperature pathway. 2nd order neuron The axon crosses obliquely to the opposite side in the anterior grey and white commissures within several spinal segments. It ascends in the contralateral white column as the anterior spinothalamic tract (ASTT). As the ASTT ascends through the spinal cord new fibers are added to the anteromedial aspect of the tract (sacral fibers are lateral and cervical fibers are medial). As the ASTT ascends through the medulla oblongata, it's joined by the lateral spinothalamic tract and the spinotectal tract and forms the spinal lemniscus. Spinal lemniscus ascends through the pons and the midbrain. Fibers of the ASTT end by synapsing with the 3rd order neurons in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus (here crude awareness of touch and pressure sensations are appreciated). 3rd order neuron Axons pass through the posterior limb of the internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the somatosensory area in the post central gyrus of the cerebral cortex. The sensations can be crudely localized. Very little discrimination is possible. Discriminative touch, vibratory sense and conscious muscle joint sense: posterior white column (fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus) 1st order neuron The axons enter the spinal cord from the posterior root ganglion and pass directly to the posterior white column of the same side. The ascending fibers travel upward in the white column as the fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus. 2! Bell’s Palsy http://bellspalsycranialnerves.wordpress.com/ Neuroanatomy Fasciculus gracilis (FG) is present throughout the spinal cord (contains ascending fibers from the sacral, lumbar and lower six thoracic spinal nerves). Fasciculus cuneatus (FC) is situated lateral to the FG in the upper thoracic and (contains ascending fibers from upper six thoracic and cervical spinal nerves). cervical segments FG and FC ascends ipsilaterally and synapses with the 2nd order neurons at medulla oblongata. 2nd order neuron The axons are called internal arcuate fibers. They decussate with the corresponding fibers from the opposite side in the sensory decussation. The fibers then ascend as a compact bundle called the medial lemniscus through medulla, pons and midbrain. The fibers synapse with the 3 rd order neuron in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. Some fibers from the FC enter the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle of the same side (cuneocerebellar tract). 3rd order neuron Axons pass through the posterior limb of the internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the somatosensory area in the post central gyrus of the cerebral cortex. Fine touch, localization, two point discrimination and vibratory sense can be recognized consciously. The main sensory pathways to consciousness 3! Bell’s Palsy http://bellspalsycranialnerves.wordpress.com/ Neuroanatomy Unconscious muscle joint sense pathways to the cerebellum 4! Bell’s Palsy http://bellspalsycranialnerves.wordpress.com/ Neuroanatomy Other ascending pathways REFERENCES: 1.# 2.# 3.# 4.# 5.# 6.# 7.# 8.# 9.# 5! Ben$Greenstein,$Ph.D,$Adam$Greenstein,$BSc$(Hons)$Mb,$ChB$Color#Atlas#of#Neuroscience Allan$Siegel$Ph.D,$Hreday$N.$Sapru$Ph.D$Essential#Neuroscience,#1st#Edition Stanley$Jacobson,$Elliot$M.$Marcus$Neuroanatomy#for#the#Neuroscientist Patrick$f.$Chinnery$Neuroscience#for#Neurologists Dale$Purves$Neuroscience,#3rd#Edition Suzan$Standring$Gray’s#Anatomy Keith$L.$Moore,$Arthur$F.$Dalley,$Anne$M.$R.$Agur$Clinically#Oriented#Anatomy Frank$H.$Netter$Atlas#of#Human#Anatomy Walter$J.$Hendelman,$M.D.,$C.M.$Atlas#of#Functional#Neuroanatomy Bell’s Palsy http://bellspalsycranialnerves.wordpress.com/