* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brainstem
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
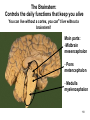
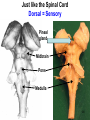
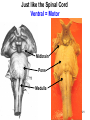
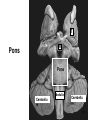
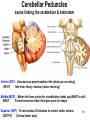
The Brainstem October 30, 2013 Chapter 13: 509 - 513 Dr. Diane M. Jaworski 117 Brainstem: does more than just link the spinal cord and cerebrum • Autonomic control of blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, pupil diameter and digestion • Cranial nerves: sensory & motor control of head/neck • Special sense nerves for hearing, balance, taste, vision • Maintains consciousness!!!!! 118 The Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that keep you alive You can live without a cortex, you can’t live without a brainstem!! Main parts: -Midbrain mesencephalon - Pons metencephalon - Medulla myelencephalon 119 Just like the Spinal Cord Dorsal = Sensory Pineal gland Midbrain Pons Medulla 120 Just like the Spinal Cord Ventral = Motor Midbrain Pons Medulla 121 122 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 T Medulla Oblongata H Pons T = Thalamus H = Hypothalamus 123 Medulla oblongata • Autonomic nuclei: - cardiovascular centers - respiratory rhythmicity centers - vomiting center 124 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 Medulla Oblongata Pyramid N cuneatus N gracilis Olive Motor info crosses here • Cranial nerves - VIII, IX, X, XI, XII • Olivary nucleus (olive) - motor learning • Pyramids - where corticospinal tract (carries descending motor info) crosses to opposite side of body • Nucleus gracilis - leg • Nucleus cuneatus - arm sensory info from body (except pain & temperature) crosses after synapsing here before going to the thalamus • Trigeminal nucleus (CN V) pain and temp from face 125 126 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 T H Pons Pons Medulla Cerebellu m Cerebellu m 127 Pons • Trigeminal nucleus (CN V) – general sensations (not pain) from the face • Motor plan sent into cerebellum for coordination (this is what makes the big bulge on the ventral pons) • Tracts: – Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) – Ascending sensory axons from body AND face 128 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 Pons • Cranial nerves - V, VI, VII, VIII 129 Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior (ICP) - Unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) INPUT Info from olivary nucleus (motor learning) Middle (MCP) - Motor info from cortex for coordination (what you WANT to do!) INPUT Forms transverse fibers that give pons its shape Superior (SCP) - To red nucleus & thalamus to correct motor actions OUTPUT (fix bad motor plan) 130 Cerebellar Peduncles Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Middle Cerebellar Peduncle 131 Transverse Fibers 132 133 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 T H Midbrain Pon s Medulla 134 Midbrain • Reticular activating system (RAS) - critical for maintaining consciousness • Substantia nigra - dopamine containing neurons that are part of the basal ganglia (motor), die in Parkinson’s disease • Red nucleus – arm flexion, damage results in a decerebrate posture which is a poor clinical sign • Cerebral peduncles – axons of descending motor neurons to innervate the brainstem and spinal cord 135 © McKinley et al. A & P 2013 Midbrain • Cerebral Peduncles Cortex motor axons going to: - Spinal cord - Brainstem cranial nerve nuclei - Pons (then to cerebellum) - Olivary nucleus (motor learning) • Red nucleus - innervates upper extremity flexor muscles Superior colliculus Inferior colliculus • Superior + Inferior Colliculi = Tectum (“roof”) • Superior colliculi - visual tracking of objects • Inferior colliculi - auditory localization • Cranial nerves - III, IV 136 Most of the Neurotransmitters for the Cerebrum are made in the Brainstem! Dopamine from the Substantia nigra Involved in movement Parkinson’s disease, drug cravings and psychosis Norepinephrine Serotonin Involved in sleep and mood Involved in control of mood, sleep and feeding 137