* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
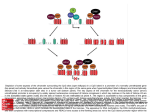
CANCER AND THE EPIGENOME In cancer cells the epigenetic landscape is highly altered. Hypermethylation of certain stretches of DNA is the most well-studied epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates and spreads. CpG Island Methyl mark Protein complexes Acetyl mark 3 4 C 1 G C CpG Shore 2 EPIGENETIC MARKS IN NORMAL CELLS A CpG island consists of a stretch of some 300 to 3,000 DNA bases where clusters of cytosine and guanine dinucleotides make up about half the sequence 1 . More than 60% of these islands are associated with the promoter regions of genes and are not methylated in genes that are actively transcribed. Located some 2 kb from these promoter regions are stretches of DNA that are not quite so rich in CpG, known as CpG shores 2 . Methylation of these cytosines results in gene inactivation and is associated with structural changes in chromatin that occur during differentiation and chromosome imprinting in developing embryos. Inactive chromatin consists of DNA tightly wrapped around a core of eight histones whose projecting tails are modified with various covalent marks 3 . Protein complexes associate with chromatin and control gene activation or repression by adding or removing marks such as methyl and acetyl groups to histones or methyl groups to cytosine bases in the DNA chain 4. G Histone tail G C DNA C G Histone C G Complex of 8 histones Accessible tumor supressor gene CpG Island Nucleosome IN Cancer When a CpG island is hypermethylated by the attachment of methyl marks to cytosines in the promoter region, transcription is halted 1 . Hypermethylation of a tumor suppressor gene results in its inactivation 2 . CpG shores are also hypermethylated in cancer cells resulting in effects on gene expression 3 . MicroRNAs (miRNA) are short pieces of RNA that are ubiquitous in eukaryotic cells. By binding to complementary sites on mRNA they act to silence genes. Hypermethylation of promoter regions of certain miRNAs involved with growth regulation has been linked to cancer and metastasis 4. RNA 4 miRNA miRNAs blocked from role in growth regulation Lost acetyl mark 2 Inaccessible tumor suppressor gene Inaccessible miRNA gene 3 Protein complexes LUCY READING-IKKANDA 1 Methylated DNA binding protein C G DNA Methyl mark C G G C C Methylated CpG island G C G 03.2011 | The Scientist | the-scientist.com 37