* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download rubric
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
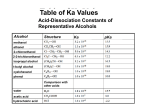
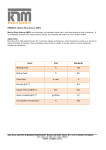
EXPLAIN how adding or removing METHYL groups can control gene expression and what role environmental influences can play in an organism’s epigenome. • Adding methyl groups to DNA turns genes off • Removing methyl groups turns genes on • Environmental influences such as: Diet, exercise, stress, chemicals can change methyl tags on DNA and change gene expression • Methyl tag patterns (epigenome) can be passed to children and even grandchildren