* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reflex action, reflex Arc, Human Brain
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
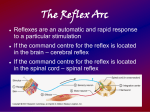
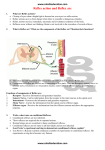
www.sakshieducation.com Reflex action, reflex Arc, Human Brain H I S 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. K S 9. 10. 11. The sudden and involuntary actions that save us from danger are _____ The structural and functional unit of a reflex action is called _____ In a reflex action the stimulus from receptor is carried to _____ In a reflex action sensory nerve carries the information to _____ in the spinal cord. The information about a stimulus is analysed by _____ of spinal cord. (Mar. 04) Interneuron's (or) association neurons play on important role in _____ actions. In a reflex action, the information from spinal cord is carried by_____ to the_____ organ. The famous Russian scientist who conducted experiments on conditioned reflexes was ____ (Mar. 07, June 02) Our standing in attention when we hear our National Anthem is a_____reflex.(Mar. 01) ___ part of the nervous systems control involuntary actions. (June 01) The neurons in the spinal cord that passes the information and generate responses are _____ The organ which receives information and generates impulses is called _____ The decade from 1990 to 2000 is known as _____ (Mar. 08, 05, 02) The weight of the brain in the total weight of the body is about _____ (Mar. 03) The organ in the body that has aesthetic sense to appreciate poetry etc. is _____ The part of the brain that helps in analyzing a problem is _____. Brain has more than _____ neurons. Brain Consumes about _____ % of total oxygen consume by the human body. Withdrawing the hand when we touch fire is _____ reflexes. _____ reflexes are inherited and shown from birth. _____ reflexes are not inherited. _____ reflexes are learnt by doing the same at several times. The human _____ is the most complicated organ in animal kingdom. Brain is solely dependent on _____ for its energy requirements. Each neuron receives 1000 to 10,000 inputs and conducts electrical impulses at a speed of _____ A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. KEY 1. Reflex actions; 2.Reflex are; 3. Spinal cord; 4. Interneurons; 5. Interneuron; 6. Reflex; 7. Motor nerves, effector organ; 8. Ivon Pavlov; 9. Conditioned reflex; 10. Spinal cord; 11.Inter neurons 12. Receptor; 13. Decade of Brain; 14. 2%; 15. Brain; 16.Cerebrum; 17. 10 billion; 18. 20%; 19. Unconditional; 20. Unconditional; 21. Conditional; 22.Conditional; 23. Brain; 24. Glucose; 25. 0.6 to 120 meters/min. www.sakshieducation.com