* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
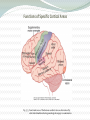
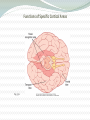
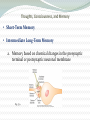
Chapter 57: Cerebral Cortex, Intellectual Functions of the Brain, Learning, and Memory Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12 edition Physiologic Anatomy of the Cerebral Cortex • Three Types of Neurons a. Granular (stellate) 1. Short axons 2. Function as interneurons 3. Excitatory with glutamate as neurotransmitter 4. Inhibitory with GABA as neurotransmitter 5. Found in the sensory areas of the cortex 6. Found in association areas between sensory and motor areas Physiologic Anatomy of the Cerebral Cortex • Three Types of Neurons b. Fusiform and Pyramidal 1. Give rise to almost all output fibers from the cortex 2. Pyramidal are larger and more numerous than fusiform 3. Pyramidal-source of nerve fibers that go all the way to the spinal cord Physiologic Anatomy of the Cerebral Cortex Fig. 57.1 Structure of the cerebral cortex, showing: I, molecular layer; II, external granular layer; III, pyramidal layer; IV, internal granular layer; V, large pyramidal cell layer; VI, layer of fusiform or polymorphic cells Physiologic Anatomy of the Cerebral Cortex • Anatomical and Functional Relations of the Cerebral Cortex to the Thalamus and Other Lower Centers Fig. 57.2 Areas of the cerebral cortex that connect with specific portions of the thalamus Functions of Specific Cortical Areas Fig. 57.3 Functional areas of the human cerebral cortex as determined by electrical stimulation during neurological surgery or examination Functions of Specific Cortical Areas • Association Areas (see Fig. 57.4) a. Parieto-occipitotemporal association area 1. Analysis of the spatial coordinates of the body 2. Wernicke’s Area-important for language comprehension 3. Angular gyrus area-needed for reading 4. Area for naming objects Functions of Specific Cortical Areas • Association Areas (see Fig. 57.4) b. Pre-frontal association area 1. Broca’s area-neural circuitary for word formation c. Limbic association area-behavior, emotions, and motivation d. Area for recognition of faces Functions of Specific Cortical Areas Fig. 57.6 Functions of Specific Cortical Areas • Comprehensive Interpretative Function of Wernicke’s Area Fig. 57.7 Functions of Specific Cortical Areas • Comprehensive Interpretative Function of Wernicke’s Area a. Angular gyrus-interpretation of visual information • Concept of the Dominant Hemisphere • Role of Language in the Function of Wernicke’s Area • Functions of the Parieto-occipitotemporal Cortex in the Nondominate Hemisphere Functions of Specific Cortical Areas • Higher Intellectual Functions of the Prefrontal Association Areas a. Decreased aggressiveness and inappropriate social behavior b. Inability to progress toward goals or carry through sequential thoughts c. Elaboration of thought-concept of a “working memory” 1. Functions of a working memory Function of the Corpus Callosum • Cutting the Corpus Callosum: a. Blocks transfer of information from the dominant hemisphere to the motor cortex on the opposite side b. Prevents transfer of somatic and visual info from the right to left hemisphere c. Person would have two entirely separate conscious portions of the brain Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Memory-Roles of Synaptic Facilitation and Synaptic Inhibition a. Positive and negative memory—sensitization or habituation of synaptic transmission b. Classification of memories 1. Declarative 2. Skill Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Declarative Memory- memory of the various details of integrated thought (i.e. memory of surroundings, time relationships, causes of experiences, meaning of an experience) • Skill Memory- associated with motor activities based on previous learning (i.e. hitting a tennis ball) Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Short-Term Memory • Intermediate Long-Term Memory a. Memory based on chemical changes in the presynaptic terminal or postsynaptic neuronal membrane Fig. 57.9 Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Molecular Mechanism of Intermediate Memory a. Mechanism of habituation-role of calcium channels b. Mechanism of facilitation-role of serotonin release and cAMP activity Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Long-Term Memory a. Structural changes in synapses during the development of long-term memory 1. Increase in vesicle release site for secretion of transmitters 2. Increase in number of transmitter vesicles released 3. Increase in the number of presynaptic terminals 4. Changes in the structure of dendritic spines that permit transmission of stronger signals Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Long-Term Memory b. Number of neurons and their connectivities change during learning • Consolidation of Memory a. Rehearsal enhances the transference of short-term memory into long-term memory b. New memories are codified during consolidation Thoughts, Consciousness, and Memory • Consolidation of Memory c. Roles of specific parts of the brain in the memory process 1. Hippocampus promotes storage of memories 2. Hippocampi not important in reflexive learning