* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sens1-General
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
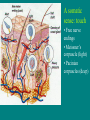
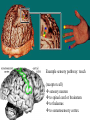
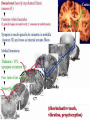
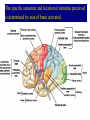
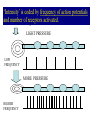
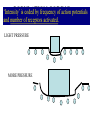
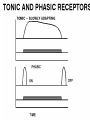
Sensory Nervous System Objectives: Describe the process of sensory transduction in general List the stimuli to which we have receptors and, for each, identify the general type of receptor Distinguish receptor potential from action potential Distinguish tonic and phasic receptor function Somatic senses fine touch, deep touch, pressure, temp, pain, joint and muscle position, muscle stretch Visceral senses pH, O2, CO2, OsM, glucose, blood pressure, lung inflation, stomach stretch Special senses olfaction, gustation, hearing, equilibrium, vision Receptors are transducers, neural or non-neural Types: chemo-, mechano-, photo-, thermo-, nociear (sense organ) with mechanoreceptors (transducers) Vestibulocochlear nerve graded potentials action potentials CNS (decoder) -medulla to thalamus to auditory cortex non-neural receptors -receptor potentials (like graded potentials) coding: which receptors are activated and AP frequency General principles of sensory function 1. Each sensory organ and receptor is specialized to convert one form of stimulus into sensory neuron action potentials. 2. Each modality has a discrete pathway to the brain. 3. The specific sensation and location of stimulus perceived is determined by area of brain activated. 4. ‘Intensity’ is coded by frequency of action potentials and number of receptors activated. Group the following senses according to whether they use chemical or mechanical receptors. -chem taste (gustation) -chem and mech pain (nociception) -chem smell (olfaction) -mech touch -mech vibration -neither vision -chem oxygen levels pressure (baroreception) -mech Which one can be both and which one is neither? A somatic sense: touch • Free nerve endings • Meissner’s corpuscle (light) • Pacinian corpuscles (deep) Example sensory pathway: touch (receptor cell) sensory neuron to spinal cord or brainstem to thalamus to somatosensory cortex General principles of sensory function 1. Each sensory organ and receptor is specialized to convert one form of stimulus into sensory neuron action potentials. 2. Each modality has a discrete pathway to the brain. 3. The specific sensation and location of stimulus perceived is determined by area of brain activated. 4. ‘Intensity’ is coded by frequency of action potentials and number of receptors activated. The specific sensation and location of stimulus perceived is determined by area of brain activated. ‘Intensity’ is coded by frequency of action potentials and number of receptors activated. FREQUENCY CODING LIGHT PRESSURE LOW FREQUENCY MORE PRESSURE HIGHER FREQUENCY POPULATION CODING ‘Intensity’ is coded by frequency of action potentials and number of receptors activated. LIGHT PRESSURE MORE PRESSURE Receptor Types Chemoreceptors : pH, O2, CO2, glucose, taste, odor, some pain Mechanoreceptors : muscle, cell, joint, lung, blood vessel and stomach stretch, sound, equilibrium Photoreceptors : light Thermoreceptors : hot or cold All receptors are transducers sensitive to a specific stimulus. Some are neurons, some are not. General principles of sensory function Somatic senses -touch, pressure, temp, pain Objectives: For each sense identify… • Any specialized structures or sense organs • Receptor type • Receptor signal transduction mechanism • Coding of intensity and duration • Pathway of conduction to the CNS • Coding for perceived sensation