* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture ppt 1 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
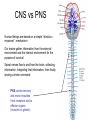
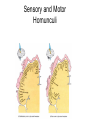
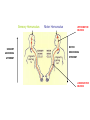
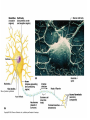
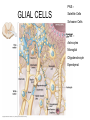
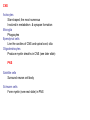
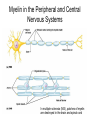
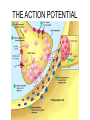
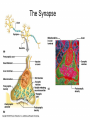
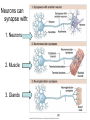
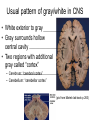
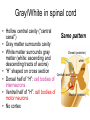
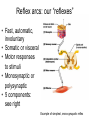
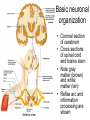
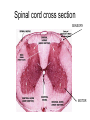
THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic CNS vs PNS Human Beings are based on a simple “stimulus – response” mechanism Our brains gather information from the external environment and the internal environment for the purpose of survival Spinal nerves flow to and from the brain, collecting information, integrating that information, then finally issuing a motor command PNS carries sensory and motor impulses from receptors and to effector organs (muscles or glands) Sensory and Motor Homunculi Sensory Homunculus SENSORY ASCENDING AFFERENT Motor Homunculus UPPER MOTOR NEURON MOTOR DESCENDING EFFERENT LOWER MOTOR NEURON Site of protein synthesis PNS – GLIAL CELLS Satellite Cells Schwann Cells CNS – Astrocytes Microglial Oligodendrocyte Ependymal CNS Astrocytes Star shaped; the most numerous Involved in metabolism & synapse formation Microglia Phagocytes Ependymal cells Line the cavities of CNS and spinal cord; cilia Oligodendrocytes Produce myelin sheaths in CNS (see later slide) PNS Satellite cells Surround neuron cell body Schwann cells Form myelin (see next slide) in PNS SCHWANN CELLS-MYELIN Myelin in the Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems In multiple sclerosis (MS), patches of myelin are destroyed in the brain and spinal cord THE ACTION POTENTIAL The Synapse Neurons can synapse with: 1. Neurons 2. Muscle 3. Glands Usual pattern of gray/white in CNS • White exterior to gray __________________ • Gray surrounds hollow central cavity ______________________________ • Two regions with additional gray called “cortex” ________________________________ – Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex” – Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex” (pic from Marieb lab book p 263) Gray/White in spinal cord • Hollow central cavity (“central canal”) • Gray matter surrounds cavity • White matter surrounds gray matter (white: ascending and descending tracts of axons) • “H” shaped on cross section • Dorsal half of “H”: cell bodies of interneurons • Ventral half of “H”: cell bodies of motor neurons • No cortex Same pattern Dorsal (posterior) white gray Central canal_____ Ventral (anterior) Reflex arcs: our “reflexes” • Fast, automatic, involuntary • Somatic or visceral • Motor responses to stimuli • Monosynaptic or polysynaptic • 5 components: see right Example of simplest, monosynapatic reflex Basic neuronal organization Anterior view • Coronal section of cerebrum • Cross sections of spinal cord and brains stem • Note gray matter (brown) and white matter (tan) • Reflex arc and information processing are shown Spinal cord cross section SENSORY MOTOR