* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structural elements and mechanisms involved in the transformation
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
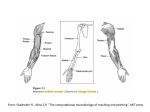
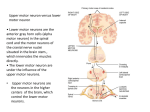
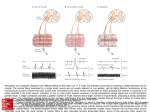
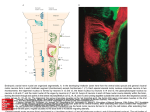
Shokoya Mariam Majida MOTOR NEURON: Cell body located in the spinal cord Axon is efferent, it carries information from the spinal cord to the effectors in the PNS (muscles and glands) Two main categories : Somatic / Visceral motor neurons Somatic motor neurons: Originate from CNS direct axons to skeletal muscles control locomotion Types of efferent motor neurons: Alpha / Beta / Gamma motor neurons Types of muscle fibers they innervate: Intrafusal / Extrafusal muscle fibers Extrafusal muscle fibers: • generate tension allow skeletal movement • mostly striated fibers attached to the bone by tendons • innervated by ALPHA motor neurons : cell body in ventral horn of the spinal cord contribute to maintain muscle tone resist further stretches Intrafusal muscle fibers: • serve as sensory organs detect the amount of change in the muscle • innervated by both sensory afferent and motor efferent neurons • Motor neurons are BETA and GAMMA beta: axon collateral to extrafusal muscle gamma: regulate sensitivity of the fiber to stretching Visceral motor neurons: indirectly innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands disynaptic command: visceral motor neuron (CNS) ganglionic neuron (PNS) visceral muscles (PNS) sypmpathetic (noradrenalin release) or parasympathetic (acetylcholin release) nerve fibers Basicly all motor neurons release acetylcholin. Neuromuscular junction: action potencial Calcium ion inflow in axon terminal fusion of synaptic vesicles release Acetylcholin postsynaptic membrane: binding to nicotinic acetylcholin receptors depolarization of muscle fiber contraction Thank you for your attention! Sources: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intrafusal_muscle_fiber https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extrafusal_muscle_fiber https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motor_neuron https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_motor_neuron https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuromuscular_junction https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/General_visceral_efferent_fibers https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle_spindle