* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carrie Heath
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
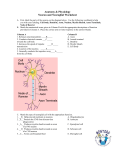
Carrie Heath Questions for the Test 1. What are the glial cells of the CNS and what are their functions? If you had to live without a particular type of glial cell, which would you pick and why? 2. What is the difference between an extracellular recording of a neuron and an intracellular recording? Give an example of how an extracellular recording could be conducted. 3. What is the function of the basal ganglia and what three nuclei constitute the basal ganglia? 4. Who invented the voltage clamp and who used it for further investigation into the movement of ions across the cell membrane? 5. What is the function of the cerebellum and the function of the cerebral cortex? How could one gather information about their functions if they were unknown? 6. Write out the Nernst Equation and the Goldmann Equation. For what reason would you use each one? 7. What experiment could be done to determine that the cell membrane of a neuron is most permeable to Potassium? 8. What experiment could you do to test the effect Sodium has on the amplitudes of peaks of action potentials? What would you find from this experiment? 9. What did Hodgekin and Huxley find when they used the voltage clamp initially? What experiment did they do to show that it was Sodium causing the inward flow of charge? 10. What two factors influence the length constant as it relates to the cable properties of the passive flow of current along the axon? 11. Explain decremental conduction and define the length constant and the time constant. 12. What are the advantages for using the squid giant neuron for experiments rather than using mammalian neurons? 13. What structures make up the blood brain barrier and what is its function? 14. What are the three input vessels and the three output vessels to the Circle of Willis? Why is this considered a defense mechanism? 15. When a neuron receives a stimulus that surpasses threshold, what allows the action potential to continue to be propagated down to the end of the axon? How is this nondecremental conduction different from decremental conduction in relation to how the current flows along the axon? 16. Explain the functions of Tetradotoxin and Tetraethylammonium. What would happen if each were separately used on the axon? What would happen if both of these chemicals were used on the axon and the neuron was subjected to a stimulus that surpassed threshold? 17. What is the importance of myelin surrounding axons and how does it relate to the length constant? How is myelin thought to be related to Multiple Sclerosis? 18. Who are the two men that invented the patch clamp technique? What are the advantages of this particular technique, and describe the four different types of recordings that can be done? 19. What is the difference between a ligand-gated ion channel and a voltage-gated ion channel? What is the most important type of ligand-gated ion channel? 20. What types of diseases are commonly caused by alterations in ion channel proteins?