* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
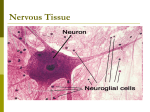
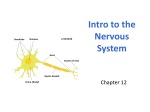
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
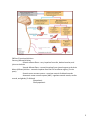
1 Master Controlling and communicating system of the body Sensory input – monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outside the body Integration – interpretation of sensory input Motor Output – response to stimuli by activating effector organs 2 PNS has 2 functional divisions Sensory (afferent) division Somatic afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain Motor (efferent) division - transmits impulses from the CNS to effector organs, (2 main parts) Somatic motor nervous system – conscious control of skeletal muscles Autonomic motor nervous system (ANS) - regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands, (2 divisions) Sympathetic Parasympathetic 3 4 Provide supportive scaffolding for neurons Segregate and insulate neurons Promote health and growth Astro=star shape Micro= small shape Epen= very close to epi meaning on top (also realated to tissues squamos or columnar) Oligodendro= dendro close to dandruff, since oligodendrocytes are white due to the myelin sheath and dandruff is also white Satellite= are the same as a regular dish satellite, the way I see it, is as if it was on a roof the same way it is on the axon Schwann = close to swan which are also white, schwann cells form myelin 5 They support and brace neurons Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies Guide migration of young neurons Control the chemical environment Best way to remember Astrocyte is by the structure and teminology. The word Astro means star, so by looking at the shape it lookes like a star. 6 Phagocytes that monitor the health of neurons Micro means small and this cell is a small defensive cell in the CNS 7 Line central cavities of the brain and spinal cord Help circulate cerebrospinal fluid with cilia Ependymal Cells you have to go back to tissues since they are ciliated and look squamous and columnar They are also related to the word epi which means on top 8 The best way to remember this cell is by comparing dendro to dandruff since they are both white do to their nature 9 Memorizing these cells are easier since they both work together. Satellite Cells actually look like they form a satellite dish, u can just picture it on top of a roof. Schwann Cells can work as white tiles of the roof itself. 10 The structural units of the nervous system Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites Long Lived, amitotic (don’t divide), and have a high metabolic rate Their plasma membrane functions in electrical signaling and cell-to-cell signaling during development 11 Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Well developed nissil bodies (rough ER) Contains an Axon Hillock – cone shaped area from which axons arise 12 Generate and transmit action potentials Secrete neurotransmitter from the axonal terminals 13 Armlike extensions from the soma Called tracts in the CNS and nerves in the PNS 14 15 Both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers are present Nodes Of Ranvier are widely spaced 16 17 Formed by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS 18 Multipolar – 3 or more processes Bipolar – 2 processes (axon and dendrite) Unipolar – single, short process 19 20 21 Sensory (afferent) – transmit impulses toward the CNS Motor (efferent) – carry impulses away from the CNS Interneurons (association neurons) – shuttle signals through CNS pathways 22 Cordlike organ of the PNS consisting of peripheral axons enclosed by connective tissue Sensory (afferent only) – carry impulses to the CNS Motor (efferent only) – carry impulses from CNS Mixed – sensory and motor fibers carry impulses to and from CNS, most common type of nerve These prefixes will be used through out the semester so remember them. Epi – (upon, on top of) always representing the outer most layer of the part being observed Peri – (around) it is usually the second layer End – (within) is the last layer, just thiks end = last 23 24