* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synapse
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
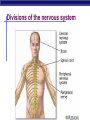
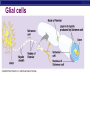
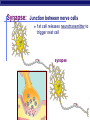
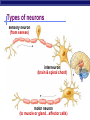
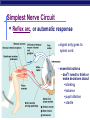
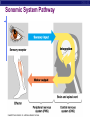
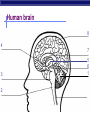
Nervous System: transport of messages in the body Divisions of the nervous system How messages travel BB A F CC E D D G G Synapse OBJ 43 Glial cells Synapse: Junction between nerve cells 1st cell releases neurotransmitter to trigger next cell synapse OBJ 45 What are some examples of neurotransmitters? Acetylcholine Epinephrine (adrenaline) Dopamine Serotonin Endorphins Types of neurons sensory neuron (from senses) interneuron (brain & spinal chord) motor neuron (to muscle or gland…effector cells) Simplest Nerve Circuit Reflex arc, or automatic response signal only goes to spinal cord essential actions don’t need to think or make decisions about blinking balance pupil dilation startle OBJ 40 Sonomic System Pathway Human brain 8 4 7 3 2 5 6 1 Drugs & the Nervous system What happens when you interfere with neural communication? Go to this website: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/ Nicotine acts as a stimulant mimics acetylcholine triggers the release of dopamine, making it addictive Alcohol Alcohol in drinks is actually ethyl alcohol High concentrations can be toxic Alcohol is a depressant Excessive amounts of alcohol damages liver, digestive system, AND NEURONS Alcohol and teens Teens’ brains are specially geared for optimal learning So, teens experience more severe damage to brain due to alcohol use (more blackouts, more brain damage…smaller brain) Drug effects What is going on when someone is addicted to drugs? Opiate drugs (heroin, morphine) can mimic endorphins (a feel-good NT) Body adjusts to higher amount of endorphinlike chemicals, and can’t do without it Take more and more of the drug. Without it, feel pain, nausea, chills, fever, depression Drug effects Marijuana (THC) – THC blocks the action of neurotransmitters in the brain affecting motor skills, memory, concentration Long-term effects: loss of memory, inability to concentrate, lowered testosterone Drug effects Ecstasy (MDMA) Causes rush of serotonin Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. Drug effects Hallucinogens LSD PCP Interfere with neurotransmitters in brain Drug effects Cocaine Causes dopamine to be released Not enough is left for normal function, so users become dependent on it Even 100 days after a cocaine addict has stopped using drugs, the decreased metabolism in the brain's frontal area remains visible. This region of the brain influences behavior such as regulating impulsive and repetitive behavior, planning and organizing activities, and critical thinking.