* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
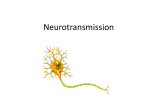
Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters Glutamate – has excitatory functions 4 Ascending activating systems are very important Cholinergic System uses acetylcholine Adrenergic system uses noradrenalin Dopaminergic system (actually 2 systems) use dopamine Serotonergic system uses 5-Ht or serotonin GABA or gamma-amino butyric acid – has inhibitory functions Acetylcholine Activate two types of receptors: Nicotinic receptors– also stimulated by nicotine and inactivated or blocked by curare Muscarinic receptors– stimulated by muscurine and blocked by atropine and scopolamine – use second messenger Monoamines Dopamine – up to 6 types of receptors Tyrosine forms L-dopa L-dopa synthesized to form dopamine Norepinephrine – created by synthesis of dopamine Epinephrine – created from Norepinephrine Serotonin (5-Ht) – synthesized from tryptophan Peptides Many types of neuropeptides; two have been extensively studied Sustance P – constriction and dilation of blood vessels Opioid types – Endorphins enkephalins How Drugs Work in the Brain They work at the level of the synapse Agonists Antagonists Possible Drug Actions at the Synapse increase or decrease the synthesis or production of neurotransmitters increase or decrease the ability of the cell to store the chemical in vesicles increase or decrease the amount of transmitter released by vesicles into the synapse it can increase the number and length of time a receptor is open by increasing or decreasing the production of enzymes that break down the neurotransmitter block or enhance the reuptake and reuse of the neurotransmitter Altering the actions of second messegers