* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BZA BCI Projects
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Guided imagery wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Functionalism (philosophy of mind) wikipedia , lookup
Neurostimulation wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
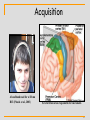
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Mental image wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoencephalography wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
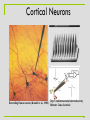
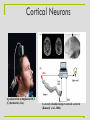
Electroencephalography wikipedia , lookup
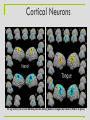
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
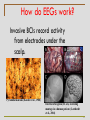
BCI Systems Brendan Allison, Ph.D. Institute for Automation University of Bremen 6 November, 2008 What is a BCI? A BCI enables communication without movement. Some patients cannot use any interface requiring movement. 2 What is a BCI? 3 What is a BCI? Most BCIs translate your brain’s electrical activity (EEGs) into messages or commands. Performing mental tasks produces electrical activity detectable with electrode caps. 4 What is a BCI? BCIs may be: • Non-invasive (usually EEG) • Invasive • ECoG (surface of cortex) • depth recording (in brain) 5 How do EEGs work? Neural communication produces electrical activity. Electrical activity in a single neuron. When a neuron is active, its voltage may change by 100 mV or more. 6 How do EEGs work? This activity may be detectable to electrodes on the scalp. Conventional electrode caps from EGI, Neuroscan, and Electro-Cap. 7 How do EEGs work? Newer EEG recording systems: • • • • • • • Require less or no prep time and skill Require less or no gel Require fewer electrodes Are more portable Handle artifacts better Are wireless Are cheaper Field recording systems from Quasar, Advanced Brain Monitoring, and Pineda et al (2003). 8 How do EEGs work? QUASAR Hybrid or eIBE sensors Audio Headset QUASAR IBE Electrodes EOG/EEG Glasses 9 How do EEGs work? Emotiv and NeuroSky systems 10 How do EEGs work? Invasive BCIs record activity from electrodes under the scalp. Pyramidal neurons (Kandel et al., 1988) Electrocorticogram (ECoG) recording montage in a human patient. (Leuthardt et al., 2004) 11 How do EEGs work? Other functional imaging approaches: • • • • Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Functional Near Infrared (fNIR) A functional MRI An MEG machine Functional Near Infrared 12 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs cannot read minds or literally interpret mental activity. yes hello pain 13 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs are a popular topic in sci fi! The Matrices Johnny Mnemonic Firefox Star Trek: The Cage Strange Days Dreamscape Neuromancer The X – Mens 14 What isn’t a BCI? More bci fi …. Total Recall Brainstorm Minority Report The Lawnmower Men The Govenator!! 15 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs cannot: • Read your thoughts. 16 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs cannot: • Operate without your knowledge or free will. 17 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs cannot: • Write to the brain. 18 What isn’t a BCI? BCIs cannot: • Repair injured areas. (??) 19 What isn’t a BCI? These similar approaches are not BCIs: ?? • • • • • • • • Biofeedback Prosthetics Retinal or cochlear implants Medical EEGs EEG or fMRI Lie Detection Neuromarketing Employee screening Attention or fatigue monitors 20 What is a BCI? BCIs rely on voluntary mental activities such as: Imagined movement Torrey Pines golf course 21 What is a BCI? BCIs rely on voluntary mental activities such as: Emotional imagery 22 What is a BCI? BCIs rely on voluntary mental activities such as: Selective attention (SSVEP) 23 What is a BCI? BCIs rely on voluntary mental activities such as: Selective attention (P300) 24 What is a BCI? BCIs rely on voluntary mental activities such as: Certain mental tasks 6 X9 42 Object rotation Math Singing 25 What is a BCI? Emerging new tasks for BCIs: • Perceived error • Imagined music • New modalities and variants (Passive BCIs): • Anticipation • Alertness/fatigue • Familiarity/recognition 26 Components How do BCIs work? o o o o General Schematic P300 BCI Mu BCI Other BCIs 27 Components A BCI requires the following: - At least 2 electrodes An amplifier designed for EEGs A mediocre personal computer An A/D card in the computer Software 28 Components All BCIs have at least four components: 1) Signal Acquisition 2) Feature Extraction 3) Translation Algorithm 4) Operating Environment The Four BCI Components (Wolpaw et al., 2002; Allison et al., 2007) 29 Components Acquisition: The user performs a task that produces a distinct EEG signature for that BCI Extraction: Salient features are extracted from the EEG Translation: A pattern classification system uses these EEG features to determine which task the user performed Environment: The BCI presents feedback to the user, and forms a message or command 30 Motor imagery: ERD 31 Acquisition Many sources create noise. Electrode cap Raw EEGs from a field setting 32 Acquisition A headband used for a 1D mu BCI (Pineda et al., 2003) Several brain areas responsible for movement. 33 Extraction, Translation Mu activity used for one dimensional control (Wolpaw et al., 1991) 34 Cortical Neurons Recording from a neuron (Kandel et al., 1988) Top: Utah intracranial electrode array Bottom: Cone electrode 35 Cortical Neurons A patient with an implanted BCI (Cyberkinetics, Inc.) A severely disabled subject controls a switch (Kennedy et al., 2004) 36 Cortical Neurons ECog activity in several human patients during hand or tongue movement (Miller, in press) 37 Selective attention: P300 EEGs from a P300 BCI 6 voltage (uV) 4 2 Nontargets 0 Targets 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 -2 -4 time after flash begins (ms) The P300 only occurs after target flashes (Allison and Pineda, 2003). 38 Environment User task: Imagine movement to move the cursor down. Relax to move it up. A mu BCI using BCI2000 (Schalk et al., 2004) 39 Acquisition, Extraction EEGs from a P300 BCI 6 voltage (uV) 4 2 Nontargets 0 Targets 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 -2 -4 time after flash begins (ms) The P300 only occurs after target flashes (Allison, 2003). It is often largest over site Cz or Pz (central or parietal areas). 40