* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation5
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
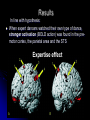
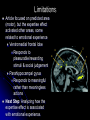
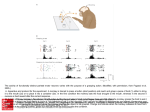
Action Observation and Acquired Motor Skills: An fMRI with Expert Dancers Article by Calvo-Merine, Glaser, Grezes, Passingham, Haggard, 2005. Presented by Stephanie Parent Introduction: key terms Action observation Observing someone performing an action •Acquired motor skills Actions that one has learned to do and mastered. The actions are integrated in the individual’s motor repertoire. •Mirror mechanism During action observation, the brain stimulate making that action by activating certain motor areas necessary to perform that action Background: Discovery of the mirror mechanism Monkey mirror mechanism (di Pelligrino, Fadiga, Fogassi, Gallese, Rizzolatti 1992) Neurons in the macaque monkey’s premotor and parietal cortices discharge Human mirror mechanism (Decety and Greze, 2001) when the monkey performs an action OR When the monkey observe an action. Premotor cortex, parietal areas and the superior temporal sulcus (STS) neurons are activated during action observation Is the mirror mechanism tuned to the individual motor repertoire? Action Observation and Acquired skills: an fMRI on expert dancers (Calvino et al., 2005) Hypothesis During action observation, the mirror system activity (pre-motor & parietal cortices and STS) will be stronger in individuals who have learned to perform that action than those who have not. Experimental task 10 professional ballet dancers, 10 Capoeira dancers and 10 non-dancers (control group) watched videos of ballet and capoeira while their brain activity was recorded in an fMRI. The difference in brain activation between expert dancers and non-expert was the point of interest Watch Results In line with hypothesis: When expert dancers watched their own type of dance, stronger activation (BOLD action) was found in the premotor cortex, the parietal area and the STS Expertise effect Discussion Implications Mirror system codes complete action patterns, not just individual movement Mirror system is sensitive to much more abstract levels of action organisation Skilled movements, meaningful movements Strengths of the article Experimental design eliminates counfounds Ballet and capoeira movements are kinetically comparable Brain activation differences are not due to differences in kinetic Dancers on video were matched in body shape and clothing and their faces were blurred Subject can’t process facial/emotional features All subjects were right-handed males aged 18-28 with normal vision and no mental illness history Diminishes individual differences Limitations Article focused on predicted area (motor), but the expertise effect activated other areas, some related to emotional experience Ventromedial frontal lobe Responds to pleasurable/rewarding stimuli & social judgement Parahippocampal gyrus Responds to meaningful rather than meaningless actions Next Step: Analyzing how the expertise effect is associated with emotional experience.