* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 6
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
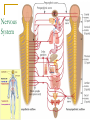
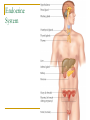
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System: Communicating Within the Body Chapter 2, Pages 63-70 Essentials of Understanding Psychology- Sixth Edition PSY110 Psychology © Richard Goldman October 4, 2006 Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System – From spinal cord to exremities Spinal Cord Conduit Reflexes Sensory (afferent) neurons Motor (efferent) neurons – (muscles) Interneuron – connect sensory to motor Peripheral Nervous System Somatic (Voluntary) – Senses & Voluntary Movement Autonomic (Involuntary) – Unconscious bodily functions Sympathetic – Prep the body for emergency (fight or flight) Parasympathetic – Calm the body Nervous System Evolutionary and Behavioral Genetics predisposes people to behave in particular ways or to have particular characteristics Endocrine System Hormones (chemical messengers) affect function and growth of parts of the body Pituitary (Master Gland) – Regulated by the hypothalamus – Responsible for growth & homeostasis Thyroid (&Parathyroid) – Metabolism Thymus – Immune system Adrenal Gland & Pancreas – Produce Insulin & Glucagon – control sugar metabolism Ovary & Testis – Produce sex hormones Endocrine System