* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain - Midlands State University
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
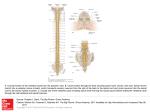
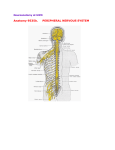
The Brain, Spinal Cord, Meninges, Cerebro-Spinal Fluid, & Nerves Obert Tada Department of Livestock & Wildlife Management Midlands State University Introduction As vertebrates evolved, the structure of their brains became more complex. The complexity is evident in the latter stages of brain development of higher vertebrates. Contents Cerebrum Interbrain Brain Stem Spinal Cord Meninges Cerebral Spinal Fluid Nerves (Spinal, Cranial, Autonomic) CNS Metabolism Structure & Function of the Vertebrate Brain The vertebrate brain develops from three anterior bulges of the spinal cord These bulges give rise to the: Forebrain Telencephalon Diencephalon Midbrain Mesencephalon Hindbrain Metencephalon Myelencephalon Cerebrum (Cerebral Hemispheres) Cortex (Gray) High Area Low Area or Groove Fissure (Deep Groove), Sulcus (Shallow Groove) Acquired late in vertebrate evolution Higher Order Functions: Consciousness/Awareness, Association/Intelligence, Learning Possesses Motor Areas (Movement) Contralateral control Size of motor area directly related to number and complexity of skeletal muscle movements Contains Sensory Areas Somesthetic, Visual, Auditory, Olfactory Cerebrum (Cerebral Hemispheres) Medullary Substance (White) Myelinated nerve fibers beneath the cerebral cortex Association fibers Connect different parts of cortex Commissural fibers Connect two hemispheres of cerebrum Projection fibers Connect Cortex with other parts of the brain and spinal chord Basal Ganglia Controls basic movement (not sophisticated) --Walking, eating, fighting, sex Well developed in birds where it controls all movements Cerebellum Makes adjustments to motor signals from the cerebrum Receives signals from: Tactile & Propioception Equilibrium apparatus of inner ear Visual cortex Motor cortex Ipsilateral control Interbrain (Diencephalon) Pituitary/Hypophysis Hypothalamus Endocrine Gland Integration of functions of the ANS (rage & anger) Homeostasis Temperature regulation, & Hunger and Thirst Thalamus Endocrine Gland Relay center from body to Cerebral Cortex Relay center of impulses within the brain Epithalamus Olfactory correlation center Pineal gland (Produces Melatonin) Seasonal Breeding, & Daily Rhythms Brain Stem Midbrain Visual Reflex Center Auditory Reflex Center Nuclei (2 Cranial Nerves) and fiber tracts Pons and Medulla Oblongata Contain many ascending and descending tracts Nuclei for rest of cranial nerves Postural reflexes Other reflex centers heart rate vasomotor tone respiration motor & secretory activity of digestive tract The Spinal Chord Caudal continuation of the medulla Segmented with vertebral segments Each segment gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves Centrally located Gray Matter "Gray H“ Cell bodies and processes Peripheral White Matter Contains sensory and motor tracts Narrows as you move caudally Terminal end--Cauda equina The Meninges Meninges of the Brain Coverings of Brain (and spinal chord) Dura Mater, Arachnoidea, & Pia Mater Subarachnoid Space contains Cerebral Spinal Fluid Pia Mater lines follows all fissures and grooves into the brain Lies between brain and blood vessels Meninges of the Spinal Chord Same make-up Epidural Space Fatty area outside Dura Mater Innervated by Spinal Nerve Projections (Roots) Used in local anesthesia Ventricles of the Brain Four Cavities in the Brain Two lateral right and left (1st and 2nd) 3rd Ventricle 4th Ventricle Surrounds Interbrain Lies beneath Cerebellum connects subarachnoid space through foramina Contain Choroid Plexus Tufts of Capillaries Secrete Cerebral Spinal Fluid Cerebral Spinal Fluid Circulation Ventricles to Subarachnoid Space to Venous Blood Pressure Driven Function Derived from Blood Plasma Principle Function --Thin and Watery --No cells except for a few lymphocytes --Brain Cushion Some Lymphatic Function Nerves (PNS) Spinal Nerves A left/right pair is derived from between every vertebra, except the coccygeal Cervical (one extra at cranial end) Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccygeal Spinal Nerves Organization i. Dorsal Root Afferent impulses (Sensory) ii. Dorsal Root Ganglion Afferent neuron cell bodies iii. Ventral Root (Motor) Efferent impulses iv. Roots join to form mixed nerve Afferent and Efferent pathways Spinal nerves supply innervations to areas dorsal and ventral to transverse process of vertebra Appendages innervated by ventral branches of several spinal nerves Join to become plexuses Cranial Nerves 12 pairs Usually innervate structures in head and neck Exception is Vagus Nerve (X) Pharynx and larynx Visceral structures of thorax and abdomen Mixed, motor, or sensory Autonomic Nerves Innervate Smooth muscle, Cardiac muscle and Glands Divisions Sympathetic Parasympathetic Generally have opposite responses Each consists of two neurons preganglionic, postganglionic Sympathetic Usually involved in "Fight, Fright, Flight" response Originate from thoracic and lumbar segments Short preganglionic, Long postganglionic Ganglionic connections form paired nerve trunk that is parallel to the spinal chord Sympathetic trunk Autonomic Nerves Parasympathetic Usually involved in tranquil or restful situations Originate from brain and sacral segments Long preganglionic, Short postganglionic Brain originators follow cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X Sacral originators follow pelvic spinal nerves Autonomic Neurotransmitter Receptors Sympathetic Norepinephrine Adrenergic Receptors Alpha 1 >>Blood vessels Beta 1 >>Heart Beta 2 >>Bronchioles Parasympathetic Acetylcholine Cholenergic Receptors Nicotinic >>Muscles Also found in Spinal, Cranial nerves and Sympathetic Nerves Muscarinic >>Organs and Tissues Autonomic Nerves Autonomic Reflex Afferent/Efferent Mechanisms Impulses do not reach conscious level Examples Blood Pressure Heart Rate Digestive and Urinary Activity Central Nervous System Metabolism Metabolism Energy from CHOs, primarily glucose Insulin not required Very high oxygen need Simple Diffusion of Glucose 20% of whole body Gray needs 3-4X more than White Matter Blood-Brain Barrier Many substance in blood can't enter cells of CNS Tight Junctions rather than Slit Pores in Endothelium Central Nervous System Metabolism Astrocytes Lie between CNS cells and Endothelium Selective to the Materials they transport Choroid Plexus Cells Also Selective Blood Requirements Higher brain can't go more than 5-10 minutes without blood Medulla -- cardiovascular and respiratory can go longer Babies can go longer without oxygen than Adults