* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System - Alamo Colleges
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
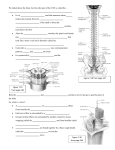
Part II Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS – all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves, associated ganglia, and motor endings Provides links to and from the external environment Sensory Receptors Mechanoreceptors –sense mechanical force (touch, pressure) Thermoreceptors –sense temperature changes Photoreceptors –sense light Chemoreceptors –respond to chemicals (taste, smell) Nociceptors –respond to pain Classes of Receptors Based on Location Exteroceptors –respond to stimuli from outside the body Interoceptors –respond to stimuli from within the body Proprioceptors –found at skeletal muscles, joints, tendons, and ligaments; keep the body aware of movements and position Nerves Nerve = bundle of axons Found only in PNS Endoneurium –surrounds each axon Perineurium –surrounds groups of axons called fascicles Epineurium –surrounds outside of entire nerve Most nerves are both sensory and motor Ganglia = cell bodies found in PNS Structure of a Nerve Figure 13.3b Cranial Nerves Associated with brain All are paired Serve only head and neck structures, except for vagus (X) Olfactory, optic, and vestibulocochlear are purely sensory Oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, accessory, and hypoglossal are purely motor The rest are mixed Olfactory Nerve (I) Arises from the olfactory epithelium Passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone Fibers run through the olfactory bulb and terminate in the primary olfactory cortex Functions solely by carrying afferent impulses for the sense of smell Optic Nerve (II) Arises from the retina of the eye Optic nerves pass through the optic canals and converge at the optic chiasm They continue to the thalamus where they synapse From there, the optic radiation fibers run to the visual cortex Functions solely by carrying afferent impulses for vision Oculomotor (III) Fibers extend from the midbrain, pass through the superior orbital fissure, and go to the extrinsic eye muscles Functions in raising the eyelid, directing the eyeball, constricting the iris, and controlling lens shape Trochlear (IV) Fibers emerge from the dorsal midbrain and enter the orbits via the superior orbital fissures; innervate the superior oblique muscle Primarily a motor nerve that directs the eyeball Trigeminal (V) Three divisions: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) Fibers run from the face to the pons via the superior orbital fissure (V1), the foramen rotundum (V2), and the foramen ovale (V3) Conveys sensory impulses from various areas of the face (V1) and (V2), and supplies motor fibers (V3) for mastication Abducens (VI) Fibers leave the inferior pons and enter the orbit via the superior orbital fissure Primarily a motor nerve innervating the lateral rectus muscle Facial (VII) Fibers leave the pons, travel through the internal acoustic meatus, and emerge through the stylomastoid foramen to the lateral aspect of the face Mixed nerve with five major branches (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical) Motor functions include facial expression, and stimulation of lacrimal and salivary glands Sensory function is taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue Vestibulocochlear (VIII) Fibers arise from the hearing and equilibrium apparatus of the inner ear, pass through the internal acoustic meatus, and enter the brainstem at the pons-medulla border Two divisions – cochlear (hearing) and vestibular (balance) Functions are solely sensory – equilibrium and hearing Glossopharyngeal (IX) Fibers emerge from the medulla, leave the skull via the jugular foramen, and run to the throat Motor – innervates part of the tongue and pharynx Sensory – fibers conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the tongue and pharynx Vagus (X) The only cranial nerve that extends beyond the head and neck Fibers emerge from the medulla via the jugular foramen Most motor fibers are to the heart, lungs, and visceral organs Its sensory function is in taste Accessory (XI) Formed from a cranial root (medulla) and a spinal root (superior spinal cord) The spinal root passes upward into the cranium via the foramen magnum The accessory nerve leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen Primarily a motor nerve Supplies fibers to the larynx, pharynx, and soft palate Innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid, which move the head and neck Hypoglossal (XII) Fibers arise from the medulla and exit the skull via the hypoglossal canal Innervates both extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue, which contribute to swallowing and speech Spinal Nerves 31 pairs (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal) Dorsal roots = sensory fibers from dorsal root ganglia, send receptive impulses to spinal cord Ventral roots = motor fibers from spinal cord, innervate skeletal muscles, send impulses from spinal cord Spinal Nerves Figure 13.6 Cervical Nerves Sensory branches – innervate skin of neck and shoulders Motor branches – innervate neck muscles Phrenic nerve – part of cervical plexus; innervates diaphragm Cervical nerves form part of brachial plexus, which innervates upper limbs Median nerve – innervates most of forearm, responsible for carpal tunnel Radial and ulnar nerves – also innervate arm and forearm Cervical Plexus Figure 13.8 Brachial Plexus: Distribution of Nerves Figure 13.9c Thoracic Nerves Mostly are responsible for innervation at each rib Each one provides a nerve supply to muscles, skin, and abdominal wall Lumbar Nerves Lumbar plexus – supplies thigh and abdominal wall Femoral nerve – nerve supply to thigh as well as part of leg Obturator nerve – nerve supply to medial thigh and adductor muscles Lumbar Plexus Sacral Nerves Sacral plexus – supplies buttocks, lower limbs and pelvis Sciatic nerve – longest nerve in body, supplies whole lower limb Tibial and fibular nerves – supply knee and leg Sacral Plexus Figure 13.11 Spinal Reflexes Not all nerve impulses travel to brain Reflex arc: Receptor – site of stimulus Sensory neuron –carries signal to spinal cord Integration center – sensory and motor neurons connected by interneurons Motor neuron – conducts impulses to effector Effector – muscle fiber or gland cell that responds to impulses Reflex Examples 1. 2. Stretch reflex – patellar reflex keeps knees straight when standing up, if pressure is applied to tendon or muscle is stretched, reflex contraction will occur Withdrawal reflex – painful stimulus causes you to withdraw from the stimulus; several muscle groups are activated Autonomic Nervous System The ANS consists of motor neurons that: Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities Operate via subconscious control Have viscera as most of their effectors Autonomic Nervous System Somatic nervous system has motor neurons which go from CNS all the way to effectors Autonomic nervous system has a chain of 2 neurons, a preganglionic neuron and a postganglionic neuron Cell body of preganglionic neuron is in CNS Cell body of postganglionic neuron is outside of CNS Postganglionic axon extends to effector Autonomic Nervous System All somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), which has an excitatory effect In the ANS: Preganglionic fibers release ACh Postganglionic fibers release norepinephrine or ACh and the effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory ANS effect on the target organ is dependent upon the neurotransmitter released and the receptor type of the effector Divisions of the ANS ANS divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic The sympathetic mobilizes the body during extreme situations The parasympathetic performs maintenance activities and conserves body energy The two divisions counterbalance each other Parasympathetic Concerned with keeping body energy use low Involves the D activities – digestion, defecation, and diuresis Its activity is illustrated in a person who relaxes after a meal Blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rates are low Gastrointestinal tract activity is high The skin is warm and the pupils are constricted Sympathetic The sympathetic division is the “fight-or-flight” system Involves E activities – exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment Promotes adjustments during exercise – blood flow to organs is reduced, flow to muscles is increased Its activity is illustrated by a person who is threatened Heart rate increases, and breathing is rapid and deep The skin is cold and sweaty, and the pupils dilate Anatomy of ANS Division Origin of Fibers Length of Fibers Sympathetic Thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord Short preganglionic and long postganglionic Parasympathetic Brain and sacral spinal Long preganglionic cord and short postganglionic Location of Ganglia Close to the spinal cord in the sympathetic trunk (chain) In the visceral effector organs Neurotransmitters and Receptors Acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrine (NE) are the two major neurotransmitters of the ANS ACh is released by all preganglionic axons and all parasympathetic postganglionic axons Cholinergic fibers – ACh-releasing fibers Adrenergic fibers – sympathetic postganglionic axons that release NE Neurotransmitter effects can be excitatory or inhibitory depending upon the receptor type Cholinergic Receptors The two types of receptors that bind ACh are nicotinic and muscarinic These are named after drugs that bind to them and mimic ACh effects Nicotinic Receptors Nicotinic receptors are found on: Motor end plates (somatic targets) All ganglionic neurons of both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla The effect of ACh binding to nicotinic receptors is always stimulatory Muscarinic Receptors Muscarinic receptors occur on all effectors innervated by parasympathetic system The effect of ACh binding: Can be either inhibitory or excitatory Depends on the receptor type of the target organ (for example, inhibits heart activity, but stimulates digestive tract activity) Adrenergic Receptors The two types of adrenergic receptors are alpha and beta Each type has two or three subclasses (1, 2, 1, 2 , 3) Effects of NE binding to: receptors is generally stimulatory receptors is generally inhibitory A notable exception – NE binding to receptors of the heart is stimulatory Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Interaction Most visceral organs are innervated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers This results in dynamic antagonisms that precisely control visceral activity Sympathetic fibers increase heart and respiratory rates, and inhibit digestion and elimination Parasympathetic fibers decrease heart and respiratory rates, and allow for digestion and the discarding of wastes CNS Control of the ANS The hypothalamus is the main integration center of ANS activity, it controls: Heart activity and blood pressure Body temperature, water balance, and endocrine activity Emotional stages (rage, pleasure) and biological drives (hunger, thirst, sex) Reactions to fear and the “fight-or-flight” system