* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pain - WordPress.com
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
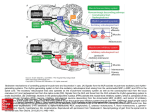
Dr.Roshith Chekkadan Dr.Rohith Chekkadan Pain is standard, evolutionary drawn pathologic process, which appears during the effect of damaging(nociceptive or algogenes) factors on organism or during weakening of antinociceptive system and is characterized by perception, activation of vegetative, emotional, behavioral, motor, antinociceptive reactions, directed to the protection of an organism from damage and to the elimination of pain. Nociceptive Neuropathic Somatic Visceral Psychosomatic Referred Phantom (illusory) the neospinothalamic tract, the paleospinothalamic tract and the archispinothalamic tract. The first-order nociceptive neurons (in the DRG) make synaptic connections in Rexed layer I neurons (marginal zone). Axons from layer I neurons decussate in the anterior white commissure and ascend in the contralateral anterolateral quadrant. Most of the pain fibers terminate in the ventroposterolateral (VPL) nucleus and ventroposteroinferior (VPI) nucleus of the thalamus.The VPL is thought to mainly be concerned with discriminatory functions. The VPL sends axons to the primary somatosensory cortex (SCI). Nociceptors—DRG—spinalcord(layer1)—crossed—LST— VPL $ VPI—SCI The majority of the first-order nociceptive neurons make synaptic connections in substantia gelatinosa(rexed layer II). Axons of second order neurons cross and ascend in the spinal cord primarily in the anterior region, called the anterior spinal thalamic tract (AST). These fibers contain several tracts. Each of them makes a synaptic connection in different locations: 1) in the mesencephalic reticular formation (MFR) and in the periaqueductal gray (PAG), and they are also called spinalreticular tract; 2) in the tectum, and these fibers are known as the spinaltectal or spinalmedullary tract; 3) in the PF-CM complex (IL) and they are known as the spinalthalamic tract). The above three fiber tracts are known also as the paleospinalthalamic tract. The archispinothalamic tract is a multisynaptic diffuse tract or pathway. The first-order nociceptive neurons make synaptic connections in Rexed layer II (substantiagelatinosa) and ascend to laminae IV to VII. From lamina IV to VII, fibers ascend and descend in the spinal cord via the multisynapticpropriospinal pathway surrounding the grey matter.Further multisynaptic diffuse pathways ascend to the intralaminar (IL) areas of the thalamus (PF-CM complex) and also send collaterals to the hypothalamus These fibers mediate visceral, emotional and autonomic reactions to pain. Pain control system in brain This system blocks the pain impulses before entering the brain. This system is present in grey matter surroundung aqueduct of sylvius and in raphe magnus nucleus in pons. The posterior grey horn is the site of pain control system of spinalcord. The posterior gray horn is the gateway for the pain impulses to reach the brain via spinalthalamic tract. During pain sensation, considerable changes occours in blood, a major one is leukocytosis. An elevation in the leucocytotic count can be observed. Reduction of nonspecific resistance after 30 minutes of acute visceral pain and restoration of protective-adaptive reactions in 3 hours occours. Thank you