* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Membrane
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
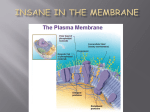
The Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Basics • Function: Controls the passage of materials into and out of a cell • Double layer of phospholipids (bilayer) Cell Membrane Basics • Function: Controls the passage of materials into and out of a cell • Double layer of phospholipids (bilayer) • Semi-Permeable: only some materials may enter/exit Phospholipid Composition • 3 Parts Polar Head • 1) Phosphate Group • 2) Glycerol phosphate glycerol Nonpolar Tails • 3) Two chains of fatty acids • Arrangement: – Outside: Polar heads Fatty (hydrophilic) acids – Inside: Nonpolar Tails (hydrophobic) – What causes this arrangement? Phospholipid Bilayer Cell Membrane Contents 1) Cholesterol: strength & flexibility 2) Carbohydrates: identification 3) Various Proteins Cell Membrane Contents glucose Protein channel glucose 1) Cholesterol: strength & flexibility 2) Carbohydrates: identification 3) Various Proteins Membrane Proteins • Randomly scattered through the bilayer • Various Functions – Cytoskeleton: internal support – Protein channels: allow objects to pass – Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions – Markers (carb chains): cell recognition; fight disease Receptor Proteins • Help cells communicate – Maintain homeostasis • Binds to ligands (molecules) – Ex: hormones and neurotransmitters • Two kinds – Membrane – Intracellular Draw, identify, label, & describe carbohydrate chain protein protein cholesterol protein channel cytoskeleton Review 1) Draw and label the basic components of the cell membrane. 2) Name the 3 parts to a phospholipid? 3) Which part(s) make up the head of a phospholipid? 4) Which part(s) make up the tails of a phospholipid? 5) Which part of phospholipid always seems to be in contact with a watery environment? Why? 6) Which membrane protein supports the cell membrane? 7) Which membrane protein allows materials to pass through? 8) What qualities/characteristics of a cell membrane help the cell to maintain homeostasis?