* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells: The living units
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
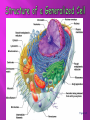
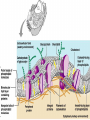
Chapter 3a Overview of the cell, and structure of the plasma membrane http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFuEo2cc TPA The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Amoebas are single-cellular Humans, dogs, trees are multi-cellular Human body has 50 to 100 Trillion cells 200 types First to observe cells Robert Hooke in 1600s (1665) (he observed cork) – Anton van Leeuwenhoek observes single cell organisms in pond water 1674 1838 Matthias Schleiden concludes all plants are made up of cells 1839 Theodor Schwann concludes all animals are made up of cells 1855 Rudolph Virchow proposed all cells come from existing cells These discoveries were very important, before ‘cell theory’ which includes all these discoveries, people accepted the theory of spontaneous generation Four concepts that are known as the Cell Theory 1. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. 2. The activity of an organism depends on the individual and collective activities of its cells 3. Principle of complementarity, (its function depends on its form) 4. Continuity of life has a cellular basis Cubelike Tilelike Disk-shaped Spherical Branching Cylindrical Figure 3.2 All cells are composed chiefly of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and trace amounts of several other elements All cells have the same basic parts and some common functions Human cells have 3 Main Parts 1. Plasma membrane 2. Cytoplasm Outer boundary of the cell Intracellular fluid packed with organelles 3. Nucleus Controls cellular activities Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Thin, Double layer (bilayer) of lipids with imbedded, dispersed proteins Bilayer consists of phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids Phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic bipoles Each phospholipid molecule has a polar ‘head’ that is charged and is hydrophilic Each phospholipid molecule has a nonpolar ‘tail’ made of 2 fatty acid chains and is hydrophobic Hydro = water Philic = loving Phobia = hating Polar heads are attracted to water so they lie on the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane Nonpolar tails avoid water and line up in the center of the membrane Plasma membranes also have proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins, and cholesterol 20% of all membrane lipid is cholesterol Cells recognize one another by markers made out of glycoproteins called Glycocalyx Small extensions of the plasma membrane that project from a free, or exposed cell surface Increases surface area Most often found on the surface of cells that function in absorption like intestinal and kidney cells Next time! Study guide check pages 53 – 55 after next lecture. http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=7204725871954420481