* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Organelles & the Cytoskeleton
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
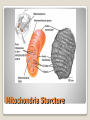
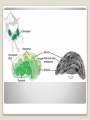
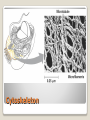
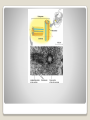
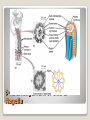
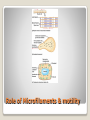
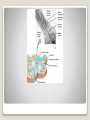
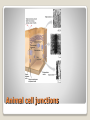
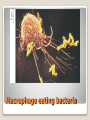
Energy Organelles & the Cytoskeleton Section 6.5, 6.6, and 6.7 Convert energy to forms the cell can use for work Mitochondria – site of cellular respiration ◦ Found in plants & animals ◦ Process that makes ATP from food ◦ Oxygen is needed Chloroplasts – site of photosynthesis ◦ Found in plants & algae only ◦ Convert solar energy to chemical energy Both enclosed by membranes Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Membranes are made on free ribosomes Contain their own ribosomes Contain a small amount of DNA Mitochondria & Chloroplast Found in all Eukaryotic cells A cell can have hundreds to thousands of mitochondria depending on its function Move around, change shape & divide Surrounded by a double membrane Outer membrane smooth Inner membrane folding (Cristae) ◦ Increases surface area Intermembrane space Matrix Mitochondria Mitochondria Sturcture Member of the plant organelle group plastids ◦ Amyloplasts – colorless that store starch in roots and tubers ◦ Chromoplasts – pigments that give fruits and flowers orange & yellow colors ◦ Chloroplasts – contain the green pigment chlorophyll Chloroplasts Double membrane separated by intermembrane space. Thylakoids are flattened stacks of sacs like pancakes or poker chips Each stack is called a granum (grana) Fluid outside the thylakoids is the stroma (space) Chloroplasts grow, move, & divide Chloroplasts Single membrane Contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substances to oxygen Hydrogen peroxide is produced (H2O2) Functions ◦ Break fatty acids down ◦ Detoxify alcohol H2O2 is converted to water because it is toxic to the cell Peroxisomes Peroxisome structure (TEM) A network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm Plays a role in organizing the structures & activities of the cell, supporting the cell, and maintaining its shape Composed of three types of structures ◦ Microtubules ◦ Microfilaments ◦ Intermediate filaments Differ in size Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton Gives support Helps the cell maintain shape Provides anchorage for organelles Can be dismantled and reassembled in a new location changing the shape of the cell Cytoskeleton - Support Changes in cell location Movements of parts of the cell Interaction of cytoskeleton with motor proteins Examples: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Movements of cilia & flagella Muscle cell contraction Movement of vesicles on “monorail” Cytoplasmic streaming Cytoskeleton - Motility Motor Proteins Cytoskeleton can transmit mechanical forces exerted by extracellular molecules via surface proteins of the cell to the interior and even the nucleus Cytoskeleton - Regulation Microtubules – thickest of the three Microfilaments – thinnest of the three Intermediate filaments – middle range size filaments 3 Types of Fibers Hollow rods Made from protein tubulin (alpha & beta) Shape and support the cell Serve as tracks for motor proteins Examples: ◦ Guide secretory vesicles from the golgi to the plasma membrane ◦ Responsible for the separation of chromosomes during cell division Microtubules Microtubules grow out from centrosomes “Microtubule-organizing center” Animal cells contain a pair of centrioles found at right angles to each other Each composed of 9 sets of triplet microtubules arranged in a ring Before the cell divides the centrioles replicate Help in organizing microtubules but not essential Plants lack centrioles Centrosomes & Centrioles Specialized arrangement of microtubules is responsible for beating of cilia & flagella Flagella ◦ 1-2 per cell, undulating motion Cilia ◦ Large numbers on cell surface, work like oars Both are made from 9+2 arrangement Dynein arms responsible for bending movements of cilia & flagella ◦ Similar to a cat walking up a tree Cilia & Flagella Motion of Flagella & Cilia 9+2 arrangement of cilia & flagella Dynein “walking” Solid rods Also called actin filaments because they are built from actin protein Twisted double chain of actin subunits Function is to bear pulling forces Part of the contractile apparatus of muscle cells Actin & myosin (thicker than actin) interact to produce muscle contraction Microfilaments (Actin filaments) Role of Microfilaments & motility Mid size filament Specialized for bearing tension Very diverse (keratins) More permanent fixtures of cells Important in reinforcing the shape of a cell and fixing the position of certain organelles Intermediate Filaments Things beyond the plasma membrane Plants – cell wall Animals – Extracellular matrix (ECM) Extracellular components Protects Maintains shape Prevents excess uptake of water Thicker than plasma membrane Strong fibers in a matrix formation like fiberglass make it extremely strong Layers of cell wall are made that include pectin (thickening agent in jams & jellies), cellulose, & hardening substances. Plant Cell Wall Glycoproteins – proteins with carbohydrate chains Collagen – accounts for ½ total protein found in the body Proteoglycans – Collagen is embedded in Fibronectin – attaches the ECM to integrins Integrins – span the membrane Important communication from the cell to its surroundings Extracellular Matrix of Animals Extracellular Matrix Plants – Plasmodesmata Channels between cell walls that allow neighboring cells to communicate with one another Water & small solutes can pass freely from cell to cell Intercellular Junctions Plant Plasmodesmata Animals ◦ Tight junctions – form continuous seals around the cells – prevent leakage ◦ Desmosomes – fasten cells together into strong sheets - anchoring ◦ Gap junctions – communicating junctions – provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell Intercellular Junctions Animal cell junctions Macrophage eating bacteria