* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure PPT Part 2
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
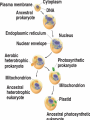
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
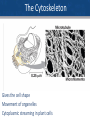
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
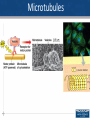
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
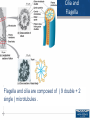
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
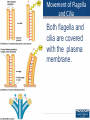
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
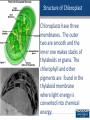
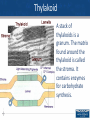
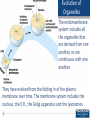
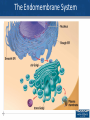
The Structure of Cell: Part II Plastids Plastids • Chromoplasts –Chloroplasts responsible for photosynthesis. • Leukoplasts responsible for storage of starch. 2 Structure of Chloroplast Chloroplasts have three membranes. The outer two are smooth and the inner one makes stacks of thylakoids or grana. The chlorophyll and other pigments are found in the thylakoid membrane where light energy is converted into chemical energy. 3 Thylakoid A stack of thylakoids is a granum. The matrix found around the thylakoid is called the stroma. It contains enzymes for carbohydrate synthesis. 4 Ribosomes Ribosomes are workbenches for protein synthesis. They are made from rRNA and proteins to form two subunits. They do not contain any membranes. Cells can have thousands. 5 Evolution of Organelles The endomembrane system includes all the organelles that are derived from one another, or are continuous with one another. They have evolved from the folding in of the plasma membrane over time. The membrane system includes the nucleus, the E.R., the Golgi apparatus and the lysosomes. 6 The Endomembrane System 7 8 The Cytoskeleton Gives the cell shape Movement of organelles Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells 9 Microtubules 10 Cilia and Flagella Flagella and cilia are composed of ( 9 double + 2 single ) microtubules . 11 Movement of Flagella and Cilia Both flagella and cilia are covered with the plasma membrane. 12 Difference Between Flagella and Cillia 13 Centrioles and Microtubules Centrioles are microtubule organizing centers for animal cells. They are constructed of nine triplet microtubules. Basal bodies anchor cilia and flagella. 14 Microfilaments Microfilaments are made from two intertwined strands of actin subunits. They are thinner than microtubules. 15 Muscle Contractions and Cytoplasmic Streaming 16 Intermediate Filaments 17 Cell Walls Most cells have materials external to the plasma membrane. Cell walls are found in prokaryotes, plants, fungi and some protists. Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose; in fungi they are made of chitin; in prokaryotes they are murein (or muramic acid) and in protists they vary. 18 Plasmodesmata Plasmodesmata are channels between plant cells that allow direct flow from one cell’s cytoplasm to the cytoplasm in adjacent cells. 19 Glycocalyx or Extracellular Matrix Animal cells lack cell walls but have an extra cellular matrix (ECM) or glycocalyx. The ECM is made of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycan, and fibronectins. These glycoproteins are connected to receptor proteins in the cell membrane called integrins. Used for support, adhesion, movement and identity. 20 Animal Cell Junctions • There are several types of intercellular junctions in animal cells • Tight junctions- membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together • Desmosomes-(anchoring junctions) fasten cells together into strong sheets • Gap junctions-(communicating junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells like plasmodesmata in plant cells 21