Axonal of Kinesin in the Chain Isoforms
... terize axonal transport of kinesin, rat retinal ganglion cells were pulse-labeled with 35S-methionine and movement of kinesin into the optic nerve, tract and tectum was monitored by quantitative immunoprecipitation. Kinesin was transported only with the fast components of axonal transport. There was ...
... terize axonal transport of kinesin, rat retinal ganglion cells were pulse-labeled with 35S-methionine and movement of kinesin into the optic nerve, tract and tectum was monitored by quantitative immunoprecipitation. Kinesin was transported only with the fast components of axonal transport. There was ...
University of Groningen Polymerization of the bacterial cell division
... conditions applied (figure 2)(101) (19, 51, 7981, 102, 104, 137, 160)(this thesis). With GTP, FtsZ assembles into thin protofilaments that are capable of assembling further into filament sheets (figure 2)(80, 102). The dynamic assembly of polymers in vitro is coupled to GTP consumption: when GTP run ...
... conditions applied (figure 2)(101) (19, 51, 7981, 102, 104, 137, 160)(this thesis). With GTP, FtsZ assembles into thin protofilaments that are capable of assembling further into filament sheets (figure 2)(80, 102). The dynamic assembly of polymers in vitro is coupled to GTP consumption: when GTP run ...
Golgins and GTPases, giving identity and structure to the Golgi
... This doesn’t mean that they are unimportant. Rather, it probably indicates that the Golgi is structurally adapted in different species to meet the specific needs of different cell types. For example, the recent finding that GM130 is not required for mammalian cell viability at 34.5 8C, but is essent ...
... This doesn’t mean that they are unimportant. Rather, it probably indicates that the Golgi is structurally adapted in different species to meet the specific needs of different cell types. For example, the recent finding that GM130 is not required for mammalian cell viability at 34.5 8C, but is essent ...
Induction and Fixation of Polarity -Early Steps in Plant Morphogenesis
... Specific and complex forms of plants and animals emerge from simple, very often symmetric, origins. This process includes a chain of basic events whereby two poles develop along an originally more or less homogeneous axis. Since the eighteenth century such phenomena are referred to by the term “pola ...
... Specific and complex forms of plants and animals emerge from simple, very often symmetric, origins. This process includes a chain of basic events whereby two poles develop along an originally more or less homogeneous axis. Since the eighteenth century such phenomena are referred to by the term “pola ...
Muscle length and myonuclear position are
... embryo shape, the intensity of the apRed and Tropomyosin signals, gut morphology, and the morphology of the trachea (Beckett and Baylies, 2007). Measurements were taken from confocal projections of embryos and acquired using the Line function of ImageJ software (NIH). For each genotype, all four lat ...
... embryo shape, the intensity of the apRed and Tropomyosin signals, gut morphology, and the morphology of the trachea (Beckett and Baylies, 2007). Measurements were taken from confocal projections of embryos and acquired using the Line function of ImageJ software (NIH). For each genotype, all four lat ...
Live Imaging of Drosophila Brain Neuroblasts Reveals a Role for
... cortex in humans. Lis1 binds dynactin and the dynein motor complex, but the role of Lis1 in many dynein/dynactindependent processes is not clearly understood. Here we generate and/or characterize mutants for Drosophila Lis1 and a dynactin subunit, Glued, to investigate the role of Lis1/dynactin in m ...
... cortex in humans. Lis1 binds dynactin and the dynein motor complex, but the role of Lis1 in many dynein/dynactindependent processes is not clearly understood. Here we generate and/or characterize mutants for Drosophila Lis1 and a dynactin subunit, Glued, to investigate the role of Lis1/dynactin in m ...
The Plant Cell - Department of Biology
... KCBP is expressed in all parts of the plant, with high expression in flowers and dividing tissues (Reddy et al., 1996b). Immunolocalization and microinjection studies with an antibody specific to KCBP indicate the involvement of KCBP in cell division (Bowser and Reddy, 1997; Smirnova et al., 1998; V ...
... KCBP is expressed in all parts of the plant, with high expression in flowers and dividing tissues (Reddy et al., 1996b). Immunolocalization and microinjection studies with an antibody specific to KCBP indicate the involvement of KCBP in cell division (Bowser and Reddy, 1997; Smirnova et al., 1998; V ...
Endoplasmic Microtubules Configure the Subapical Cytoplasm and
... results and allowed the study of MTs during hair development. Cortical MTs (CMTs) are present in all developmental stages. During the transition from bulge to a tip-growing root hair, endoplasmic MTs (EMTs) appear at the tip of the young hair and remain there until growth arrest. EMTs are a specific ...
... results and allowed the study of MTs during hair development. Cortical MTs (CMTs) are present in all developmental stages. During the transition from bulge to a tip-growing root hair, endoplasmic MTs (EMTs) appear at the tip of the young hair and remain there until growth arrest. EMTs are a specific ...
Cytoskeleton and Root Hair Growth
... Root hairs are highly polarized outgrowths of a subset of root epidermis cells, the socalled trichoblasts. The biological function of root hairs is to increase the surface area of roots in order to facilitate the absorption of water and nutrients from soil. Root hairs are also the site of initial in ...
... Root hairs are highly polarized outgrowths of a subset of root epidermis cells, the socalled trichoblasts. The biological function of root hairs is to increase the surface area of roots in order to facilitate the absorption of water and nutrients from soil. Root hairs are also the site of initial in ...
Cytoplasmic and cortical reorganizations of the ascidian zygote
... A definition of the myoplasm as a cytoplasmic domain The myoplasm has been loosely defined as a cortical/subcortical region of the egg and zygote which when relocalized and/or transferred is associated with the differentiation of muscle cells. It presumably contains a muscle determinant which can be ...
... A definition of the myoplasm as a cytoplasmic domain The myoplasm has been loosely defined as a cortical/subcortical region of the egg and zygote which when relocalized and/or transferred is associated with the differentiation of muscle cells. It presumably contains a muscle determinant which can be ...
Interaction of Antiparallel Microtubules in the
... vesicles began to accumulate at the division site, long MTs were frequently detected in the phragmoplast formed between two reforming daughter nuclei (Figure 1A). Although many MTs were terminated in regions where vesicles accumulated, others crossed the midline and overlapped (Figures 1A and 1B). S ...
... vesicles began to accumulate at the division site, long MTs were frequently detected in the phragmoplast formed between two reforming daughter nuclei (Figure 1A). Although many MTs were terminated in regions where vesicles accumulated, others crossed the midline and overlapped (Figures 1A and 1B). S ...
Dynamics of Tubulovesicular Recycling Endosomes in Hippocampal
... To determine the subcellular localization of syntaxin 13 in neuronal cells, we stained embryonic and postnatal cultured hippocampal neurons with affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies raised against syntaxin 13. In both neuronal cultures syntaxin 13 was detected in small puncta throughout the cell, ...
... To determine the subcellular localization of syntaxin 13 in neuronal cells, we stained embryonic and postnatal cultured hippocampal neurons with affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies raised against syntaxin 13. In both neuronal cultures syntaxin 13 was detected in small puncta throughout the cell, ...
A Review of Centriole Activity, and Wrongful Activity, during Cell
... sides of the nucleus then begin to pull the nucleus apart. As the nucleus is being elongated the microtubules of the centrioles extend and align themselves along the long axis of the nucleus, forming the “mitotic spindle” [61] [83] [98]-[102], as represented in Figure 4. The nucleus then shrinks in ...
... sides of the nucleus then begin to pull the nucleus apart. As the nucleus is being elongated the microtubules of the centrioles extend and align themselves along the long axis of the nucleus, forming the “mitotic spindle” [61] [83] [98]-[102], as represented in Figure 4. The nucleus then shrinks in ...
The Presynaptic Microtubule Cytoskeleton in Physiological and
... kinases, casein kinases, and tyrosine kinases (MacRae, 1997). Interestingly, it has been shown that calcium–calmodulin kinase (CamKII) is a protein kinase that interacts with SVs in presynaptic terminals (Benfenati et al., 1996; Ninan and Arancio, 2004), and directly phosphorylates both α-tubulin an ...
... kinases, casein kinases, and tyrosine kinases (MacRae, 1997). Interestingly, it has been shown that calcium–calmodulin kinase (CamKII) is a protein kinase that interacts with SVs in presynaptic terminals (Benfenati et al., 1996; Ninan and Arancio, 2004), and directly phosphorylates both α-tubulin an ...
Chromosome Segregation in Budding Yeast: Sister Chromatid
... Figure 2 Chromosome segregation during meiosis. Schematic diagram showing the key features of chromosome segregation during budding yeast meiosis. ...
... Figure 2 Chromosome segregation during meiosis. Schematic diagram showing the key features of chromosome segregation during budding yeast meiosis. ...
Hereditary spastic paraplegia: clinical features and pathogenetic
... HSP associated with mutations in the gene for heat shock protein 60 (HSPD1; formerly SPG13) typically has a late onset without additional features.26 A Gly563Ala missense variant was recently reported to be associated with an earlier age of onset in patients carrying SPAST mutations, although this w ...
... HSP associated with mutations in the gene for heat shock protein 60 (HSPD1; formerly SPG13) typically has a late onset without additional features.26 A Gly563Ala missense variant was recently reported to be associated with an earlier age of onset in patients carrying SPAST mutations, although this w ...
Tetrazine−trans-cyclooctene Mediated Conjugation of Antibodies to
... several limitations, including aggregation due to the multimeric nature of streptavidin,17,18 cargo loss due to a decreased lifetime of the bonds under tension19 as well as at high gliding velocities,20 and reduced velocity of transport.21 The noncovalent biotin−streptavidin interaction is short-ran ...
... several limitations, including aggregation due to the multimeric nature of streptavidin,17,18 cargo loss due to a decreased lifetime of the bonds under tension19 as well as at high gliding velocities,20 and reduced velocity of transport.21 The noncovalent biotin−streptavidin interaction is short-ran ...
Requirements for CPC localization during anaphase
... Figure 2: Schematic representation of the CPC. Interactions within the complex are represented by white arrowheads. Survivin and Borealin interact with the N terminus of INCENP, Aurora B interacts with the IN box of INCENP, which is at the C terminus of INCENP. Borealin and Survivin also bind ...
... Figure 2: Schematic representation of the CPC. Interactions within the complex are represented by white arrowheads. Survivin and Borealin interact with the N terminus of INCENP, Aurora B interacts with the IN box of INCENP, which is at the C terminus of INCENP. Borealin and Survivin also bind ...
PDF
... Fig. 1. Clathrin negatively regulates net pulling forces acting on centrosomes during centration/rotation and on spindle poles during anaphase. (A-G) Centration/rotation. (A,B) Centrosome position in wild-type (A) and chc-1(RNAi) (B) embryos monitored by time-lapse DIC microscopy. Centrosomes are ma ...
... Fig. 1. Clathrin negatively regulates net pulling forces acting on centrosomes during centration/rotation and on spindle poles during anaphase. (A-G) Centration/rotation. (A,B) Centrosome position in wild-type (A) and chc-1(RNAi) (B) embryos monitored by time-lapse DIC microscopy. Centrosomes are ma ...
FtsZ - Cytoskeleton, Inc.
... cell division. FtsZ inactivation inhibits cell division, making them attractive targets for novel anti-microbial drugs. Although FtsZ proteins exhibit a degree of homology, inhibitors of the proteins show differential affinities and efficacies. Thus, improved targeting can be achieved by screening s ...
... cell division. FtsZ inactivation inhibits cell division, making them attractive targets for novel anti-microbial drugs. Although FtsZ proteins exhibit a degree of homology, inhibitors of the proteins show differential affinities and efficacies. Thus, improved targeting can be achieved by screening s ...
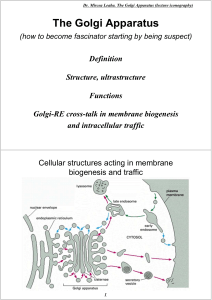
The Golgi Apparatus
... 1. Labeling of lysosomal enzymes, in cis area 2. Transport from cis-face toward trans-face, and maturation 3. Sorting and budding, in trans area, as primary lysosomes 4. Fusion with late endosomes or already existing secondary lysosome ...
... 1. Labeling of lysosomal enzymes, in cis area 2. Transport from cis-face toward trans-face, and maturation 3. Sorting and budding, in trans area, as primary lysosomes 4. Fusion with late endosomes or already existing secondary lysosome ...
Pericentriolar material structure and dynamics
... kinase prevents accumulation of g-tubulin at centrosomes and mitotic PCM expansion in humans, flies and worms (figure 2) [23,40,41,67,68]. Furthermore, polo kinase has been demonstrated to directly phosphorylate the core scaffold proteins pericentein, Cnn and SPD-5, and mutation of polo phosphorylat ...
... kinase prevents accumulation of g-tubulin at centrosomes and mitotic PCM expansion in humans, flies and worms (figure 2) [23,40,41,67,68]. Furthermore, polo kinase has been demonstrated to directly phosphorylate the core scaffold proteins pericentein, Cnn and SPD-5, and mutation of polo phosphorylat ...
Type-IV Antifreeze Proteins are Essential for Epiboly and
... characterized by the conserved four-helix bundle [24-26], and the antifreeze activity has been demonstrated in several fishes [23-26]. Significantly, along with wide discoveries of afp4 homologues, their abundant expression has been detected recently in oocytes [27, 28] and in embryos [20] from some ...
... characterized by the conserved four-helix bundle [24-26], and the antifreeze activity has been demonstrated in several fishes [23-26]. Significantly, along with wide discoveries of afp4 homologues, their abundant expression has been detected recently in oocytes [27, 28] and in embryos [20] from some ...
PDF version
... complex comprised of Gα (GOA-1/GPA-16), GPR-1/GPR-2, and LIN-5 is essential for anchoring the motor protein dynein to the cell cortex, where it is thought to exert pulling forces on depolymerizing astral microtubules. We proceed by providing an overview of cell cycle asynchrony in two-cell embryos, ...
... complex comprised of Gα (GOA-1/GPA-16), GPR-1/GPR-2, and LIN-5 is essential for anchoring the motor protein dynein to the cell cortex, where it is thought to exert pulling forces on depolymerizing astral microtubules. We proceed by providing an overview of cell cycle asynchrony in two-cell embryos, ...
Force generation by kinesin and myosin cytoskeletal motor proteins
... kinesins is adjacent to a region containing loop L8, which also binds microtubules, it is possible that movements in switch I provide a second, distinct pathway of communication between the nucleotide-binding site and the microtubule-binding interface, allowing for fine-tuning of the kinesin mechano ...
... kinesins is adjacent to a region containing loop L8, which also binds microtubules, it is possible that movements in switch I provide a second, distinct pathway of communication between the nucleotide-binding site and the microtubule-binding interface, allowing for fine-tuning of the kinesin mechano ...
Microtubule

Microtubules (micro- + tube + -ule) are a component of the cytoskeleton, found throughout the cytoplasm. These tubular polymers of tubulin can grow as long as 50 micrometres and are highly dynamic. The outer diameter of a microtubule is about 24 nm while the inner diameter is about 12 nm. They are found in eukaryotic cells and are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin.Microtubules are very important in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella.They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, organelles, and intracellular macromolecular assemblies (see entries for dynein and kinesin). They are also involved in chromosome separation (mitosis and meiosis), and are the major constituents of mitotic spindles, which are used to pull apart eukaryotic chromosomes.Microtubules are nucleated and organized by microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), such as the centrosome found in the center of many animal cells or the basal bodies found in cilia and flagella, or the spindle pole bodies found in fungi.There are many proteins that bind to microtubules, including the motor proteins kinesin and dynein, severing proteins like katanin, and other proteins important for regulating microtubule dynamics.