* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
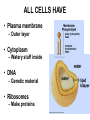
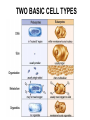
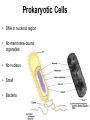
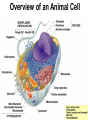
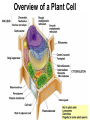
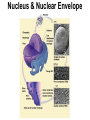
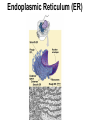
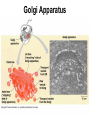
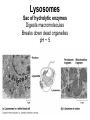
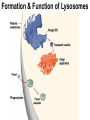
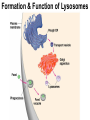
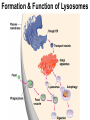
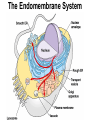
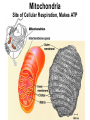
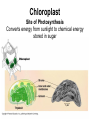
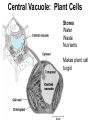
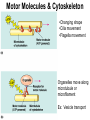
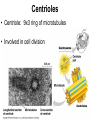
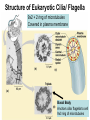
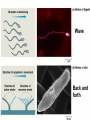
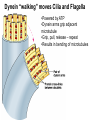
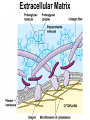
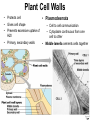
Cells Chapter 7 The size range of cells Why are cells so small? Small cells have a high surface area to volume ratio which allows more stuff to move in and out of the cell CELL THEORY • Living organisms are composed of one or more cells • Cells are the smallest unit of life • Cells come from other cells ALL CELLS HAVE • Plasma membrane – Outer layer • Cytoplasm – Watery stuff inside • DNA – Genetic material • Ribosomes – Make proteins TWO BASIC CELL TYPES Prokaryotic Cells • DNA in nucleoid region • No membrane-bound organelles • No nucleus • Small • Bacteria Plasma Membrane aka: The Gate-keeper Overview of an Animal Cell Overview of a Plant Cell Nucleus & Nuclear Envelope Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Sac of hydrolytic enzymes Digests macromolecules Breaks down dead organelles pH ~ 5 Formation & Function of Lysosomes Formation & Function of Lysosomes Formation & Function of Lysosomes The Endomembrane System Mitochondria Site of Cellular Respiration, Makes ATP Chloroplast Site of Photosynthesis Converts energy from sunlight to chemical energy stored in sugar Central Vacuole: Plant Cells Stores Water Waste Nutrients Makes plant cell turgid Peroxisomes Produce and break down H2O2 Cytoskeleton • Network of fibers throughout cytoplasm • Gives cell shape • Holds organelles in place • Involved in movement & changing shape Motor Molecules & Cytoskeleton •Changing shape •Cilia movement •Flagella movement Organelles move along microtubule or microfilament Ex: Vesicle transport Centrioles • Centriole: 9x3 ring of microtubules • Involved in cell division Structure of Eukaryotic Cilia/ Flagella 9x2 + 2 ring of microtubules Covered in plasma membrane Basal Body Anchors cilia/ flagella to cell 9x3 ring of microtubules Wave Back and forth Dynein “walking” moves Cilia and Flagella •Powered by ATP •Dynein arms grip adjacent microtubule •Grip, pull, release – repeat •Results in bending of microtubules Microfilaments (actin filaments) • Pulling force – Muscle contraction – Cytoplasmic streaming – Pseudopodia • Part of Extracellular Matrix – Support cell membrane – Inside of cell membrane Extracellular Matrix Plant Cell Walls • Protects cell • Plasmodesmata • Gives cell shape – Cell to cell communication • Prevents excessive uptake of – Cytoplasm continuous from one H20 cell to other • Primary, secondary walls • Middle lamella cements cells together Cell Junctions in Animal Cells Fuses membranes Strong sheets Pass ions and small molecules