* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
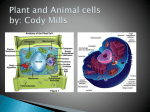
2.1 The Structure & Functions of Eukaryotic Cells Chloroplasts • Derived from photosynthetic bacteria & has DNA • A double membrane bound, solar energy capturing organelle • Internal thylakoid membrane is stacked (grana) and has pigments for photosynthesis. • Liquid medium around thylakoid called stroma. Chloroplast Micrograph Photosynthesis • It takes place in the thylakoid membranes and stroma • Pigments like chlorophyll capture solar energy to make cellular food (ie: glucose) • Cyanobacteria closely related to chloroplasts in higher plants. Mitochondria • Have their own DNA • A double membrane bound organelle • Internal cristae membrane is folded for increased surface area. • Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the cristae and the matrix • The liquid medium inside the cristae is called the matrix. Mitochondria Micrograph Mitochondria • Breaks down high-energy organic molecules (cellular respiration) to store in chemical bonds as chemical potential energy. • In addition to glucose, it can also use lipids and proteins • The released energy is stored in the form of ATP Cell Walls • It is found in plants, fungi, & many protists • Surrounds cell membrane for support and protection (ie: Turgor Pressure in plants) • Made of either polysaccharides, glycoproteins or both. • It is porous and does little to control access to the cell. Cytoskeleton • It is an internal network of protein fibres • It’s made of 3 fibre types – Microfilaments – Microtubules – Intermediate filaments • 3 functions: – mechanical support – anchors organelles – help move substances Microfilament Micrograph Cell Movement • Microtubules & microfilaments - slide against one another for internal cell movement • Cilia – Short – Used to move substances outside human cells • Flagella – Whip-like extensions – Found on sperm cells Cilia & Flagella Structure • • • • Both are extensions from the cell membrane. They’re bundles of microtubules Cilia are short and in large numbers for movement. Flagella are few but longer for locomotion. Cell (Plasma) Membrane • It wraps the cell contents & it’s semi-permeable. • It’s a double layer of phospholipids & embedded proteins • This “fluid mosaic model” has the hydrophillic heads oriented to the outside and hydrophobic tails to the inside. This controls access in & out of the cell. • Includes cholesterol, glycoproteins and glycolipids. Cell Membrane Micrograph Phospholipids • They are lipid molecules with one glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group. • The polar head is hydrophyllic head and the non-polar tail is hydrophobic. • Most of the fatty acid chains are saturated. Membrane Proteins 1. Channels or transporters – Move molecules in one direction 2. Receptors – Recognize certain chemicals Membrane Proteins 3. Cytoskeleton – Microtubules & microfilaments 4. Enzymes – Catalyze production of substances End Part 3