* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles and Functions Powerpoint
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
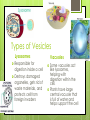
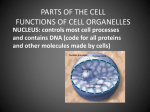
Parts of a Cell http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=- zafJKbMPA8 Cell Wall A rigid structure that gives support to a cell Found in plant cells, algae, fungus and prokaryotes Plant and algae cells have cell walls made of cellulose Fungus have cell walls made of chitin Cell Membrane All cells have a cell membrane Cell membrane is a protective barrier that encloses a cell. It separates the cell’s contents from the cell’s environment Outermost structure of a cell, unless there is a cell wall. Contains proteins, lipids, and phospholipids Cell membrane cont’d Some of the proteins and lipids control the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Nutrients and water move into the cell, and wastes move out of the cell, through the protein passageways. Cytoskeleton A web of proteins in the cytoplasm. Acts as both a muscle and a skeleton. Keeps the cell’s membranes from collapsing. Also helps some cells move. Made of 3 types of protein. One protein is a hollow tube, the other two are long, stringy fibers Nucleus Large organelle in a eukaryotic cell that contains the cell’s DNA Covered by two membranes. Materials cross this double membrane by passing through pores. Many cells have a dark area in the nucleus called the nucleolus – which is where a cell begins to make its ribosomes. Ribosomes Organelle that makes proteins. Smallest of all organelles More ribosomes in a cell than any other organelle. Some float freely in cytoplasm, others are attached. Do not have a membrane. Endoplasmic Reticulum A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materials are made. Contains many tubes and passageways, which substances move through to different places in the cell 2 kinds of endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER Rough ER and Smooth ER Rough ER Covered in ribosomes Usually found near the nucleus The ribosomes make the proteins that are sent through the ER to other parts of the cell Smooth ER Does not have ribosomes Makes lipids and breaks down toxic materials that could damage the cell Mitochondria Main power source of the cell Covered by 2 membranes Breaks down sugar to produce energy The energy released by mitochondria is stored in a substance called ATP. The cell then uses the ATP to do work. Most ATP is made in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Chloroplasts Organelles in PLANT AND ALGAE cells in which photosynthesis takes place Has 2 membranes and make their own DNA They are green because they contain chlorophyll, which is found inside the inner membrane of a chloroplast. Chlorophyll traps the energy of sunlight, which is used to make sugar. The sugar produces is then used by mitochondria to make ATP Golgi Complex Organelle that packages and distributes proteins Looks like smooth ER Lipids and proteins from the ER are delivered to the Golgi Complex. Then the lipids and proteins may be modified to do different jobs. The final product is enclosed in a piece of the GC’s membrane. This membrane pinches off to forma small bubble, which transports the contents to other parts of the cell Vesicles Small sac that surrounds materials to be moved into or out of a cell, or within a cell The small part of the Golgi complex that pinches off is a vesicle All eukaryotic cells have vesicles Vesicles carry new protein from the ER to the Golgi Complex Vesicles distribute material from the Golgi Complex to other parts of the cell Types of Vesicles Lysosomes Responsible for digestion inside a cell Destroys damaged organelles, gets rid of waste materials, and protects cell from foreign invaders Vacuoles Some vacuoles act like lysosomes, helping with digestion within the cell. Plants have large central vacuole that is full of water and helps support the cell