* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles - Taran D. Thompson
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
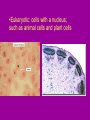
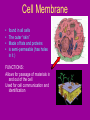
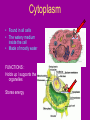
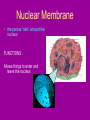
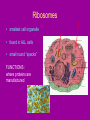
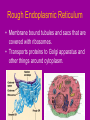
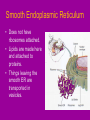
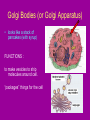
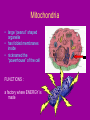
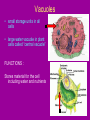
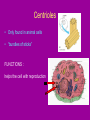
Cell Organelles microscopic “organ – like” structures that help the cell to function Two types of cells • Prokaryotic: cells without a nucleus; such as Bacteria •Eukaryotic: cells with a nucleus; such as animal cells and plant cells Cell Membrane • • • • found in all cells The outer “skin” Made of fats and proteins is semi-permeable (has holes in it ) FUNCTIONS: Allows for passage of materials in and out of the cell Used for cell communication and identification Cell Wall • a tough outer coat • found in ONLY plant cells & some bacteria cells FUNCTIONS : Adds extra protection and support to plant cells Cytoplasm • Found in all cells • The watery medium inside the cell • Made of mostly water FUNCTIONS : Holds up / supports the organelles Stores energy Cytoskeleton • Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. • The cytoskeleton helps to support the cell and maintain its shape • It is made up of microtubules and microfilaments. Nucleus • found in all EUKARYOTIC cells (plants, animals, fungi and protists) • Largest organelle FUNCTIONS : Has DNA inside Is the “control” center of the cell Bacteria cells do not have one = PROKARYOTES Nucleolous • found inside the nucleus FUNCTIONS : Has RNA inside Gives instructions for the making of protein Nuclear Membrane • the porous “skin” around the nucleus FUNCTIONS : Allows things to enter and leave the nucleus Ribosomes • smallest cell organelle • found in ALL cells • small round “specks” FUNCTIONS : where proteins are manufactured Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Membrane bound tubules and sacs that are covered with ribosomes. • Transports proteins to Golgi apparatus and other things around cytoplasm. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Does not have ribosomes attached. • Lipids are made here and attached to proteins. • Things leaving the smooth ER are transported in vesicles. Golgi Bodies (or Golgi Apparatus) • looks like a stack of pancakes (with syrup) FUNCTIONS : to make vesicles to ship molecules around cell. “packages” things for the cell Mitochondria • large “peanut” shaped organelle • has folded membranes inside • nicknamed the “powerhouse” of the cell FUNCTIONS : a factory where ENERGY is made Chloroplasts • found ONLY in plant and some protists cells • green football-shaped organelles FUNCTIONS : to make food for plant cells through the process of photosynthesis Lysosomes • nicknamed “suicide packets” • has digestive acids inside • has a double lined membrane FUNCTIONS : helps the cell to digest food ***can burst and kill itself *** Vacuoles • small storage units in all cells • large water vacuole in plant cells called “central vacuole” FUNCTIONS : Stores material for the cell including water and nutrients Centrioles • Only found in animal cells • “bundles of sticks” FUNCTIONS : helps the cell with reproduction Cilia and Flagella • Found in prokaryote and eukaryote cells. • Made of microtubules and help different cells move. • Cilia and flagella differ in their beating patterns