* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Articles about the Brain Works
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
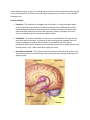
Articles about the Brain Works Disclaimer: If possible, please show this document on a smartphone or computer to avoid printing. Source: National Geographic Kids Neurons send info to your brain at more than 150 miles (241 kilometers) per hour. A bee lands on your bare foot. Sensory neurons in your skin relay this information to your spinal cord and brain at a speed of more than 150 miles (241 kilometers) per hour. Your brain then uses motor neurons to transmit the message back through your spinal cord to your foot to shake the bee off quickly. Motor neurons can relay this information at more than 200 miles (322 kilometers) per hour. When you learn, you change the structure of your brain. Riding a bike seems impossible at first. But soon you master it. How? As you practice, your brain sends "bike riding" messages along certain pathways of neurons over and over, forming new connections. In fact, the structure of your brain changes every time you learn, as well as whenever you have a new thought or memory. Source: www.ducksters.com Biology for Kids The Human Brain The brain is where we do our thinking. All our senses are tied into our brain allowing us to experience the outside world. We remember, have emotions, solve problems, worry about stuff, dream about the future, and control our bodies in our brain. For such an awesome organ, the brain doesn't look like much. It's a ball of gray looking wrinkled tissue about the size of two of your fists put together. The brain sits in our hard, thick skull with membranes and fluid around it to protect it. How the Brain Communicates The brain is part of the nervous system. Together with the spinal cord, it makes up the central nervous system. The brain connects to nerves that travel throughout the body. Nerves from our senses (hearing, seeing, touch, etc.) send signals to the brain to let the brain know what is going on in the outside world. The brain also sends signals using nerves to muscles in order to make our body move. Parts of the Brain Cerebrum - The cerebrum is the biggest part of the brain. It's the gray wrinkly upper part. The surface of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex. Different parts of the cerebrum deal with different parts of the body. The back part deals with vision while other parts deal with other functions like movement, hearing, language, and touch. Smart or thinking people are sometimes called cerebral. Cerebellum - At the back and bottom of the brain is the cerebellum. This part of brain deals with motor movement. It processes all the incoming motor messages from the nerves and figures out what to do with them. The cerebellum can learn motor movements with practice allowing us to do stuff like riding a bike or typing without even thinking about it. Hey, I didn't think about typing this once! Brain Stem or Medulla - This is where the brain connects to the spinal cord. Also, many automatic functions are controlled here like keeping the heart beating, breathing, and digesting food. Memory The brain has two kinds of memory, short term memory and long term memory. Scientists are still learning exactly how memory works, but they know that short term memory allows us to remember something for a very short time without rehearsing or practicing it. We can't remember a lot of things in short term memory though, and, like its name suggests, these memories don't last very long. The Brain Needs Energy The brain may not move, but it needs lots of energy. Energy is sent to the brain by our blood. There are lots of blood vessels and blood flowing through the brain at all times. The brain actually uses around twenty percent of the body's energy. The Brain Has Two Halves The brain is divided into two halves. Since the nerves cross when they enter the brain, the left side of our brain controls the right half of our body and the right side controls the left. Each half also controls specialized functions. What each half does depends on whether you are left or right handed. In a right handed person the left side of the brain is used for language and numbers while the right side is the more artistic side and is also used for recognizing objects. Source: Women’s and Children’s Health Network What is the brain? The brain is the control center for your body and it sits in your skull at the top of your spinal cord. The brain has three main parts. 1. The cerebellum (say se-re-bell-um). 2. The cerebrum (say se-re-brum), which has two parts, the left and right cerebral hemispheres, (say se-re-brell hem-iss-fears). 3. The brain stem controls a lot of the 'automatic' actions of your body, such as breathing and heartbeat, and links the brain to the spinal cord and the rest of the body. Your brain is wrapped in 3 layers of tissue and floats in a special shock-proof fluid to stop it from getting bumped on the inside of your skull as your body moves around. What the brain does Your brain is more powerful, more complex and more clever than any computer ever built. It is constantly dealing with hundreds of messages from the world around you, and from your body, and telling your body what to do. It gets the messages from your senses – seeing, hearing, tasting, smelling, touching and moving. The messages travel from nerve cells all over the body. They travel along nerve fibers to nerve cells in the brain. Cranial nerves (say cray-nee-al) carry messages to and from the ears, eyes, nose, throat, tongue and skin on your face and scalp. The spinal cord carries messages to and from the arms, legs and trunk of the body. Sensory nerves collect the information and send it to the brain along one network then motor nerves take the brain's orders back along another network (like cars travelling along their own side of the highway.) Your brain collects all the information, sorts it out, thinks, remembers, creates, compares, solves problems and coordinates actions all at the same time - even when you're asleep! (And you don't have to be 'plugged in' and 'online' either!) If you get too tired or don't eat enough food, your brain can't do this as well as usual. Control centers of the brain Doctors and scientists have found that different parts of the brain are in charge of different things. Look at the diagram for an easy way to understand. The cerebellum controls and coordinates movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don't fall over when you turn around. The outside layer of the cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and personality. The brain stem is in charge of keeping the automatic systems of your body working. You don't have to think about breathing, you just do it automatically, but you can decide if you want to hold your breath for a short time. You don't have to think about your heart beating because your brain keeps it going automatically. Interesting facts about the human brain Do you know that your brain has around 100 billion nerve cells? It also has 1,000 billion other cells, which cover the nerve cells and the parts of the nerve cells which form the links between one cell and another, feed them and keep them healthy. Your brain keeps on growing until you are about 20 years old. By then the brain has made lots of links which it no longer needs so it is able to shed any unwanted connections and still have billions of brain cells left to cope with whatever you may want to do. You can still make new connections even when you are 100 years old, so get Grandma going on the computer - she may not learn as fast as you but she can do it! The front of the human brain is larger than any other animal's, even the dinosaurs! The left side of your brain is usually better at problem solving, math and writing. The right side of the brain is creative and helps you to be good at art or music. The brain stores all sorts of things in the memory including facts and figures and all the smells, tastes and things you have seen, heard or touched. Your brain can also find things that you have remembered---like how to spell ce-re-bell-um. The adult brain weighs about 1.5kg. Looking after your brain Your brain is protected inside your skull but could still be damaged if your head is hit or bumps into something hard. Eating healthy food like fish and fresh vegetables. Exercising your brain by learning new things and trying to remember them. Getting plenty of sleep. Dr. Kim says The human brain is so complex that doctors and scientists still don't know what some parts of it do. They do know that if the brain is damaged, the damage often cannot be repaired. You can't join brain cells together like you can do with bones. Doctors and scientists know how some of the brain works and can sometimes fix it when things go wrong, but the brain is truly amazing and we don't know all its secrets yet.