* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interspersed Repetitive Noncoding DNA
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
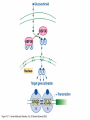
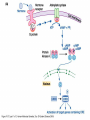
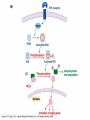
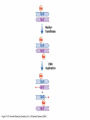
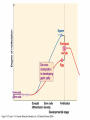
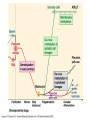
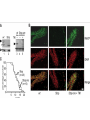
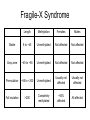
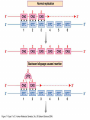
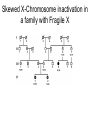
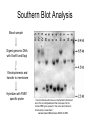
YORK UNIVERSITY Department of Biology Faculty of Science and Engineering Course outline Human Molecular Genetics (SC/BIOL 4285 3.0) W2015 Prerequisite: SC/BIOL 3130 1 Instructor: Dr. Michael Scheid Rm. 236 Farqharson Building Website: scheid.blog.yorku.ca E-mail: [email protected] Office hours: Tuesday/Thursday 10:15-11:00 am 2 STUDENT EVALUATION: There will be ONE Midterm exam, worth 30% of your grade: Midterm – February 13 You will submit a RESEARCH PAPER, worth 20% of your grade: Paper – due March 27 The FINAL EXAM will be worth 50% of your grade. 3 Please note : There will be NO MAKE-UP of the midterm exams. For medical issues please have your physician fill out the Attending Physician Statement. This form is available from the Registrars website. 4 Academic Integrity: Senate Policy on Academic Dishonesty Students are expected to be familiar with and follow York University’s Policies regarding academic integrity. Please consult the website below for more details: http://www.yorku.ca/academicintegrity/students.htm 5 • ACADEMIC MISCONDUCT WILL NOT BE TOLERATED. • Cheating is the attempt to gain an improper advantage in an academic evaluation. Forms of cheating include: – Obtaining a copy of an examination before it is officially available or learning an examination question before it is officially available; – Copying another person’s answer to an examination question; – Consulting an unauthorized source during an examination; – Obtaining assistance by means of documentary, electronic or other aids which are not approved by the instructor; – Changing a score or a record of an examination result; – Submitting the work one has done for one class or project to a second class, or as a second project, without the prior informed consent of the relevant instructors; – Submitting work prepared in collaboration with another or other member(s) of a class, when collaborative work on a project has not been authorized by the instructor; – Submitting work prepared in whole or in part by another person and representing that work as one’s own; – Offering for sale essays or other assignments, in whole or in part, with the expectation that these works will be submitted by a student for appraisal; – Preparing work in whole or in part, with the expectation that this work will be submitted by a student for appraisal. 6 Overview of Gene Expression • Mechanisms to control gene expression • Spatial/temporal consideration Overview of Gene Expression • RNA Polymerase II – Transcription factors and cis-acting regulatory sequences Overview of Gene Expression • Ligand-inducible transcription factors – examples 10_11.jpg 10_12.jpg 10_12_2.jpg Overview of Gene Expression • Epigenetic regulation 10_18.jpg 10_19.jpg 10_19_2.jpg Paula Quintero-Ronderos and GladisMontoya-Ortiz Autoimmune Diseases Volume 2012, Article ID 593720, 16 pages DNA Methylation • Host defense vs. Gene regulation • Parent of origin: imprinting • Biallelic vs monoallelic expression • Inappropriate DNA methylation can cause problems • eg. Cancer • Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome DNA Methylation • Determine the biological role of methylation • Disrupt genes involved – DNMT (DNA methyltransferase) Li E, et al. Cell, 1992, 69:915-26. “Homolgous knockout of DNA methyltransferase in mice leads to embryonic lethality.” DNA Methylation • Determine the biological role of methylation • Disrupt genes involved – methyl-bindingdomain proteins (eg MeCP2) Tate, P., Skarnes, W. & Bird, A. Nature Genet. 12, 205-208 (1996). “The methyl-CpG binding protein MeCP2 is essential for embryonic development in the mouse.” Rett Syndrome • Occurrence: 1 in 10,000 Neuron, November 2007, Pages 422-437 Rett Syndrome • In humans, MeCP2 is mutated in 1 in 10,000 females • Causes severe neurological disorders • Rett Syndrome Rett Syndrome Rett Syndrome • 80% of females with Rett syndrome have mutations in MeCP2 • Example of a strong single-gene disorder • Result of inappropriate loss of gene silencing Inappropriate Silencing of Genes • Fragile-X Syndrome Fragile-X Syndrome Length Methylation Females Males Stable 6 to ~45 Unmethylated Not affected Not affected Gray zone ~45 to ~55 Unmethylated Not affected Not affected Premutation ~55 to ~200 Unmethylated Usually not affected Usually not affected Full mutation >200 Completely methylated ~50% affected All affected 11_05.jpg 11_05_2.jpg Skewed X-Chromosome inactivation in a family with Fragile X Southern Blot Analysis Blood sample Digest genomic DNA with EcoRI and EagI Electrophoresis and transfer to membrane Hybridize with FMR1 specific probe “A normal female will show an unmethylated 2.8-kb band and a 5.2-kb methylated band that correspond to the normal FMR1 gene present in the active and inactive X chromosome, respectively.”