* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The autonomic nervous system
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
The autonomic nervous system
Stellek Bálint Sándor
2016.10.27.
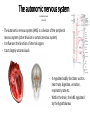
- The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a division of the peripheral
nervous system (other division is somatic nervous system)
- It influences the function of internal organs
- It acts largely unconsciously
- It regulates bodily functions such as
heart rate, digestion, urination,
respiratory rate etc.
- Within the brain, the ANS regulated
by the hypothalamus
- The autonomic nervous system is divided into two
part:
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Emerges from the spinal cord in the thoracic
and lumbar areas ("thoracolumbar outflow”)
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- It has “craniosacral outflow”, meaning that
the neurons begin at the cranial nerves and
sacral spinal cord.
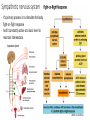
Sympathetic nervous system
- It’s primary process is to stimulate the body's
fight-or-flight response
- And it constantly active at a basic level to
maintain homeostasis.
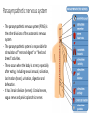
Parasympathetic nervous system
- The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is
the other divisions of the autonomic nervous
system
- The parasympathetic system is responsible for
stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and
breed” activities.
- These occur when the body is at rest, especially
after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation,
lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion and
defecation.
- It has 3 main division (nerves): Cranial nerves,
vagus nerve and pelvic splanchnic nerves
- Two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the
sympathetic and parasympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic
- Ganglion is a nerve cell cluster or a group of nerve cell bodies located in the
autonomic nervous system. Ganglia house the cell bodies of afferent nerves.
- In the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, efferent nerve signals
are carried from the central nervous system to their targets by a system of two
neurons.
- The axons of preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are usually long, extending
from the CNS into a ganglion that is either very close to or embedded in their
target organ (sympathetic is the opposite).