* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download kumc 05 nervous system review student
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
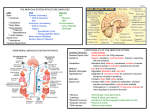
ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS SENSORY MOTOR COGNITIVE ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM Nervous System CNS PNS ANS BRAIN CRANIAL NERVES SYMPATHETIC SPINAL CORD SPINAL NERVES PARASYMPATHETIC Central Nervous System (CNS) Unpaired, bilaterally symmetrical structures extending along the longitudinal axis of the midsagittal plane of the body. Structures arising directly from the neural tube. Includes: Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Made up of transmission pathways carrying information between the CNS and external/internal environments. Afferent (sensory) pathways: Carry information to the CNS. Efferent (motor) pathways: Carry information from the CNS. Peripheral Nervous System Includes: Cranial nerves (12 pairs) Spinal nerves (31 pairs) Also includes sensory receptors in skin and wall of gut tube as well as in tendons and skeletal muscles. Also includes motor end plates between motor neurons and skeletal muscle fibers. Autonomic Nervous System May be considered a subdivision of the PNS. Entirely motor. Innervates smooth muscle and glands (viscera) ANS Subdivisions Sympathetic system (fight or flight) Also called thoracolumbar Parasympathetic system (feed and breed) Also called craniosacral Parts of a Neuron Cell body: Trophic unit Perikaryon Dendrites: Receptive unit Axon: Conductive unit Cell Body That part of a neuron that encloses the nucleus and other organelles necessary to maintain and repair neuron. Cell Body Organelles Nucleus Golgi apparatus RER Ribosomes =Nissl substance Dendrites Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. Axon That part of the neuron that carries information to another neuron or muscle cell. Usually relatively long. Single. Conducts action potential (nerve impulse) Axon Ends in short branched processes called: Telodendria: Give off endings called terminal boutons. Terminal boutons contain synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters. May have collateral branches. Axon Cell membrane is called the axolemma. Cytoplasm is called the axoplasm. Axon Contains: Mitochondria Neurofilaments Neurotubules Axonal Transport Anterograde Retrograde Slow transport Fast transport Axon Covered by neurolemma: Made up of Schwann cells. Often myelinated: Myelin is formed by Schwann cells. Note: axon is only part of neuron that is ever myelinated. General Terminology Nucleus: Aggregation of dendrites and nerve cell bodies in the CNS. Ganglion: Aggregation of dendrites and nerve cell bodies in the PNS. General Terminology Nerve: Bundle of fibers (axons) in the PNS. Tract: Bundle of fibers (axons) in the CNS. Commissure: Tract in the CNS that crosses from one side to the other. General Terminology White matter: Areas of myelinated axons. Gray matter: Areas of unmyelinated axons, cell bodies, and dendrites. Functions of the CNS Refer to p. 63 in syllabus Spinal Nerve Branches Dorsal primary ramus Ventral primary ramus Ramus recurrens White ramus communicans Gray ramus communicans Spinal Nerve Branches Paravertebral ganglion Splanchnic nerve Prevertebral ganglion Reflex Arc Afferent (sensory) pathways: Somatic. Visceral (splanchnic). Efferent (motor) pathways: Somatic. Visceral (splanchnic). Association neurons (interneurons). Synapse Components: Presynaptic membrane: With synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. Synaptic cleft: Postsynaptic membrane: With receptors for neurotransmitters. Monosynaptic pathways. Polysynaptic pathways.