* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
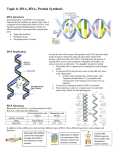
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid “The Blueprint of Life” I. DNA Structure & Function A. What is DNA? 1. Organic molecule 2. Nucleic acid B.Where is it located? 1. Nucleus 2. Chromosomes Chromosomes in Nucleus C. Structure of DNA Nucleotides a. Phosphoric Acid b. Deoxyribose sugar c. Nitrogenous bases: Adenine-Thymine Guanine-Cytosine 2. Ladder Shape 3. Double strand, helix twist Ladder Shape (Sides & Rungs) Sides: Phosphoric Acid Sugar Phosphoric Acid Rungs: A-T T-A G-C C-G Watson & Crick’s Double helix: D. What is DNA’s Function? Hereditary Instructions Chemical code for every trait “Blueprint” for making Proteins - Proteins are groups of amino acids linked together and folded up. - Proteins are responsible for all of the traits that living things possess. Chromosome DNA Code: Genes = Segments of DNA Code for a trait DNA Chromosome Code: Triplets= Sets of 3 Nucleotides Code for Trait DNA Chromosome Code: DNA Replication Chromosomes double Mitosis Late Interphase 2n to 4n E. Steps for DNA Replication: DNA untwists DNA unzips Corresponding base pairs Line up In sets of 3 nucleotides (triplets) aka “codons” DNA reforms 2 strands twist into double helix RNA Ribonucleic Acid “DNA messenger & taxi” II. RNA Structure & Function A. What is RNA? Organic Molecule Nucleic Acid mRNA = messenger RNA tRNA = transfer RNA B. Where is RNA located? mRNA in nucleus & cytoplasm tRNA only in cytoplasm B. What is RNA’s structure? Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base Nucleotides= a. Phosphoric Acid b. Ribose sugar c. Nitrogenous Bases: Adenine-Uracil Guanine-Cytocine 2. Single Strand 3. No Twisted helix RNA Structure vs. DNA Structure Comparison of RNA & DNA: Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base Acid Sugar-Base D. What are RNA’s functions: mRNA= Copies the DNA code Deliveries message to Ribosome Protein Factories Why not send the original DNA code out? DNA might be damaged! mRNA components are reused To copy more messages RNA function cont. tRNA: in cytoplasm Picks up an amino acid “Taxis” the aa to the Ribosome protein factories III. Protein Synthesis Assembling Proteins from the DNA Instructions. Proteins are chains of amino acids folded up. A. Transcription: mRNA is copied off of DNA In nucleus Steps: DNA untwists DNA unzips RNA codons line up Transcription: mRNA has: Ribose sugar Uracil instead of thymine bases Nuclear membrane allows it to leave! B. Translation = Conversion of the message (mRNA Code) into a protein By the ribosome factories Codon – 3 bases on the mRNA that code for an amino acid. Anticodon – 3 bases on the tRNA that code for an amino acid – follow base pairing rules for the codon. Translation Steps mRNA arrives at the Ribosome tRNA picks up an amino acid tRNA delivers the aa to the ribosome aa are assembled into polypeptide proteins Translation Breaking the Genetic Code (See Genetic Code Handout) Scientists can use two tables that reference the genetic code. We can read the codons in a strand of mRNA and use the charts to tell us what amino acids will be added to the polypeptide chain. Summary: DNA Replication: Make duplicate DNA In nucleus Copy the chromosomes For Mitosis Protein Synthesis: Transcrition: Make mRNA From DNA Translation: Make protein - Off mRNA code - Using amino acids