* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Distinguish between mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. What molecule does
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
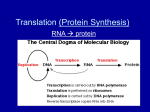
Chapter 8 Sandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike Reilly Question: Distinguish between mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. What molecule does each abbreviation represent and what role does each molecule play in the process of gene expression? Describe and explain. RNA’s mRNA – messenger RNA tRNA – transfer RNA rRNA – Ribosomal RNA mRNA - encodes proteins Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) is a copy of the information carried by a gene. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosome. htttp://www.biochem.uwo.ca The "life cycle" of an mRNA in a eukaryotic cell www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the central component of the ribosome's protein manufacturing machinery. rRNA are sub cellular structures that are composed of another kind of RNA. Each ribosome is composed of 2 subunits 1 large and 1 small when assembled it can bind to structures called Transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying amino acids. Work Cited: Biology science for life. www.biology.unm.edu Transfer RNA (tRNA) tRNA - adaptor, binds amino acids and rRNA and translates between mRNA and protein. Each tRNA also carries the amino acid corresponding to the mRNA codon to which it binds. Transfer RNA translates the language of nucleotides into the language of amino acids. tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosomes during translation to be assembled into polypeptide chains. tRNAs are encoded by tRNA genes. All tRNA molecules are similar in size and shape. All tRNAs have CCA at the 3' end to which the amino acid attaches. At the other "end" of the tRNA molecule is the anticodon, which, during translation, "reads" the matching codon on the mRNA. www.phschool.com