* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download anti-codon
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
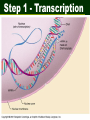
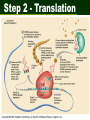
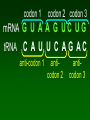
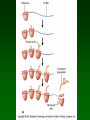
Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs Turned into Review Proteins - long chains of amino acids Order of amino acids important because • it determine the shape of protein • which in turn determine the function or job of protein Protein Differences w/ DNA • Single strand of nucleotides • nucleotide URACIL replaces thymine Complimentary bases in RNA 1. cytosine & guanine 2. adenine & uracil 3 types of RNA in protein syn. 1. mRNA - messenger RNA • Straight single strand of RNA 2 . tRNA - transfer RNA • Club shaped - transport amino acids 3. rRNA - ribosomal RNA - help link amino acids together 3 steps protein synthesis 1. Transcription - DNA mRNA 2. Translation - tRNA reads mRNA 3. Linking - amino acids linked together Step 1 - Transcription code form DNA used to form mRNA • in nucleus • DNA unzipped - base pairs read • Complimentary RNA nucleotides form mRNA Step 1 - Transcription Original DNA C A T T C A G A C mRNA G U A A G U C U G formed codon • Code is stored - groups of 3 nucleotide basepairs - called a CODON Step 2 - Translation mRNA enters cytoplasm & ribosomes read codons on mRNA Step 2 - Translation tRNA - carry amino acids • has special region - ANTI-CODON -- 3 nucleotides • nucleotides complimentary to codons on mRNA • determine amino acid tRNA carries codon 1 codon 2 codon 3 mRNA G U A A G U C U G tRNA C A U U C A G A C anti-codon 1 anticodon 2 anticodon 3 Step 3 - Linking Amino acids brought to ribosome by tRNA - linked together tRNA w/ complimentary anticodon - fits into ribosome - drops off amino acid attached & links to protein chain codon 1 codon 2 codon 3 mRNA G U A A G U C U G tRNA C A U U C A G A C anti-codon 1 Amino Valine acid (Val) anticodon 2 anticodon 3 Serine (Ser) Leucine (Leu) • STOP codon - on mRNA stops linking amno acids • START codon - start linking amino acids