* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
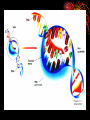
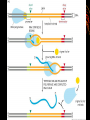
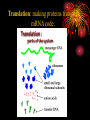
RNA •Ribonucleic acid •single stranded •also made of nucleotides RNA nucleotides •Sugar (ribose) •Phosphate •nitrogenous base •adenine •cytosine •guanine •uracil Types of RNA •mRNA: messenger RNA, carries the DNA code out of the nucleus to the ribosome •tRNA: transfer RNA, carries amino acids to the ribosome •rRNA: ribosomal RNA, part of the ribosome Transcription (making RNA) 1. DNA unzips 2. one strand of DNA acts as a template 3. RNA polymerase reads the DNA bases 3’ to 5’ 4. RNA nucleotides are placed across from the complimentary DNA bases 5. RNA separates from DNA 6. DNA zips back up mRNA processing 1. Methylated guanine cap added to 5’ end 2. Poly-A tail added to 3’ end of mRNA 3. Introns (non-coding RNA) are removed 4. Exons (coding RNA) are spliced together mRNA Processing • 5’ cap • 3’ AAAAAAA “poly-A” tail • Introns removed, exons spliced together http://www.arabidopsis.org/servlets/sv?action= accession&type=gene&id=2204897&chr=1 Click on this link and click on the sequence ruler to view genetic sequence with introns, exons etc. Protein Synthesis or How to Make Your Own Proteins •mRNA: messenger RNA - singlestranded, brings the DNA message out of the nucleus. •tRNA: transfer RNA – single-stranded but looped around to be shaped like a “t”. brings an amino acid to a ribosome to build a protein. •Transcription: making mRNA. RNA polymerase (enzyme) reads one strand of unzipped DNA, and makes mRNA using the order of the DNA bases. •mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores. In the cytoplasm, mRNA is read by ribosomes. Translation Translation: making proteins from the mRNA code. Translation: making proteins from the mRNA code. •mRNA enters a ribosome. •One tRNA molecule brings one amino acid to the ribosome. •Another tRNA brings another amino acid and the 2 amino acids form a peptide bond. •The first tRNA leaves the ribosome and the 2nd tRNA shifts over. •This growing polypeptide chain will become a protein. •The order of amino acids is vital to the formation of proteins. •How does the ribosome and tRNA know the order of amino acids? •It’s in the order of bases on the mRNA. •Every 3 bases on mRNA is a codon. •A codon specifies an amino acid. •There are also codons which mean stop making the protein and a codon which means start. •The 3 codon bases of mRNA correspond to 3 bases on tRNA called the anticodon. •tRNA molecules have different anticodons which identifies which amino acid it carries to the ribosome.