* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
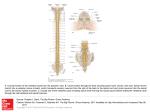
JOSE S. SANTIAGO M.D. Nervous System CNS (central nervous system) Spinal cord Brain Peripheral nervous system Sensory neurons Motor neurons 2 Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input – gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed Functions of the Nervous System Motor output A response to integrated stimuli The response activates muscles or glands Nerve Cells Neurons Cell body Axon Some have myelin sheath Dendrites 5 Neuron Anatomy Cell body Nucleus Large nucleolus Figure 7.4a Neuron Anatomy Extensions outside the cell body Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body Figure 7.4a Nerve Cells Neuroglia Do not carry electrical impulses Protect the neurons by phagocytosis Provide nutrients 8 Synapses Synapse Electrical impulse transmission Gap between neuron and a muscle or between two neurons 9 Synapses Neurotransmitters of the peripheral nervous system Released from sac at end of neuron Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine 10 The Brain Part of the CNS Cerebrum Hemispheres divided by longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum connect the hemispheres Cerebral cortex 11 The Brain Cerebrum Gyri (convolutions) Sulci and fissures Lobes Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital 12 Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum) The surface is made of ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci) Figure 7.13a Brain 14 Brain Thalamus Hypothalamus 15 Brain Brain stem Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Cerebellum 16 The Spinal Cord Part of the CNS Starts at the medulla oblongata and ends at the conus medullaris 17 The Spinal Cord 31 pairs of nerves 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal 18 Spinal Cord Meninges - protective membranes Dura mater-tough, protective connective tissue; tightly bound to the skull; encases the cerebral veins 19 Spinal Cord Arachnoid mater- web-like strands of connective tissue Pia mater- thin permeable membrane 20 Spinal Cord Subdural space Subarachnoid space- contains CSF and arteries Cerebrospinal fluidsecreted by the choroid plexus Blood-brain barrier 21 Spinal Cord Blood-brain barrier- protection for the brain against undesirable blood substances 22 Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves 12 pairs Emerge bilaterally from base of the skull Spinal nerves 31 pairs Emerge bilaterally from the spinal cord 23 Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise Additional Word Parts – Roots Myelin/o 25 myelin sheath Roots Cerebell/o 26 cerebellum Roots Cerebr/o 27 brain Roots Cortic/o 28 cortex; outer covering Roots Dur/o 29 dura mater Prefixes Pachy- thick Pachymeninx- dura mater 30 Roots Encephal/o -brain Encephalitisinflammation of the brain 31 Roots Magnet/o-magnet Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)produces picture of brain using magnetic waves 32 Roots Hydr/o -water Hydrocephalusaccumulation of fluid in the brain 33 Roots Ventricul/o- ventricles Ventricles-hollow cavities inside the brain 34 Roots Vertricul/o- ventricles Ventriculostomy -new opening in the ventricles; for treating hydrocephalus 35 Suffixes -oma -tumor Hematomaaccumulation of blood in a space Epidural hematoma-blood in the epidural space 36 Suffixes -oma -tumor Hematomaaccumulation of blood in a space Subdural hematoma-blood in the subdural space 37 Types of Brain Hematoma THANK YOU!