* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromatin DNA Methylayion
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
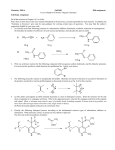
The bilateral interrelationship between chromatin and DNA methylation and its impact on cancer The bilateral interrelationship of chromatin and DNA methylation • DNA methylation is a reversible reaction, the DNA methylation pattern is a balance of methylation and demethylation. • Active demethylation is directed by chromatin structure • Proteins that inhibit histone acetylation inhibit demethylation, a mechanism for regional hypermethylation in cancer. • MBD2/demethylase is essential for tumorigenesis. • MBD2/demethylase controls genes required for invasion. DNA methylation aberrations in cancer cells • Certain few genes are regionally hypermethylated • The genome is globally hypomethylated DNA Methylation inhibits gene expression by two independent mechanisms CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 AP 2 CH3 CH3 Myc/Max CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 MECP2 MECP2 mSin3A HDAC Model 1: DNA methylation patterns are fixed during development maintained faithfully by the maintenance methyltransferase in somatic cells CH3 CH3 devlopment CH3 CH3 CH3 Site specific demethylation CH3 CH3 CH3 mature cells CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 maintenance methylation CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 An Ectopically Methylated Reporter Gene is Demethylated when it is Directed by an Active Promoter CA T Acetylated Chloramphenicol (dpm) SV40 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 SV40CAT pMetCAT 20000 0 CA T Promoter Constructs pMet Model 2: The steady state methylation pattern is a dynamic equilibrium between methylase and demethylase activities CH3 active CH3 CH3 inactive inactive methylase demethylase CH3 CH3 active CH3 The direction of the arrow is determined by interacting factors that determine the state of activity of the gene TSA CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 HAT binding X CH3 CH3 TSA Enhances Processive Demethylation of GFP DpnI HpaII Dpn I EGFP +TSA pCMV Hpa II Xba I -TSA +TSA A TC G ATC G CMV-GFP does not replicate in HEK293 cells therefore demethylation must be active TSA induces demethylation of a promotererless GFP DNA therefore demethylase does not require specific promoter binding sites Time and TSA dose dependence of active demethylation TSA induced demethylation is not a consequence of alteration in cell cycle kinetics EGFP pCMV control Serum starved +TSA Sequences associated with acetylated histones are actively demethylated +TSA CMVGFP SV40CAT +TSA - TSA -TSA NO IP CONTROL NO IP CONTROL Anti H3 IP +TSA Anti H3 IP + TSA Anti H3 IP -TSA +TSA MetCAT -TSA TSA CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 HAT binding X CH3 CH3 Why do certain housekeeping genes become hypermethylated in cancer? • Why doesn’t TSA induce demethylation of all genes? – A number of methylated tumor suppressors were shown not to be induced by TSA. Hypothesis: certain proteins bind to specific promoters and inhibit histone acetylation and demethylation. Inhibitors of Acetyltransferases (INHAT subunits) Inhibit Acetylation Through Histone Masking ? K CH3 CH3 TAF-1∂ TAF-1ß INHAT K CH3 CH3 CH3 Set/Taf1-b inhibits histone acetylation and expression of CMV-GFP Histone acetylation: Set/TaF1-b Set/TaF1-b 120-225 Set/TaF1-b H3 H2B H2A H4 CMV-GFP expression Set/TaF1-b coomasie phosphorimage Set/TaF1-b 120-225 GFP-Westen blot Amido black The INHATs Set/Taf1-b and pp32 inhibit TSA induced demethylation of GFP sequences 100 50 Dose dependent inhibition of GFP demethylation by Set/Taf-1b but not DSet/Taf1-b -TSA DSet/Taf1-b 100 % demethylation Set/Taf1-b DSet/Taf1-b 50 Set/Taf1-b 0.5 1 1.5 Dose µg 2 DNA bound to INHATs is protected from demethylase, DNA bound to acetylated histones is demethylated Input IP -acetylHistone Set/TAF-1ß The epigenome is guarded by the interdependence of DNA methylation and histone acetylation TF TR HAT HDAC demethylase INHATs DNMT TSA Set/TAF-1ß Oncogene Message is Significantly Increased in Multiple Tumor Tissues 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0 4 3 2 1 0 4 3 2 1 0 breast 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 stomach colon 3 2 1 0 rectum 1.2 0.8 0.4 0 kidney total 1.0 average 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 normal p<0.00039 uterus tumor MBD MBD2/demethylase1 MBD3/demethylase2 PLC Coiled coil motif domain Amino acid sequence of demethylase 1 and 2 Demethylase assay demethylase activity CH 3 CH 3 * * * CpGpCpGpCpGpCpGpCpG GpC pGpCp GpCp GpC CH 3 CH 3 Cp* Cp* Cp* Cp* Ectopic expression of Mbd2bhis-dMTase induces demethylation of GFP reporter sequences CMV-GFP Promoterless-GFP MBD2/demethylase activates specific promoters but not others in a time dependent manner Dose dependent activation by MBD2/demethylase Ectopic expression of MBD2/demethylase increases global demethylase activity in HEK cells Expression of MBD2/demethylase increases demethylation at the SV40 promoter Mechanisms of protection of the epigenome: DNA replication DNA methylation slow Histone acetylation demethylation (stable) transient and fast slow Histone deacetylation methylation (stable) Regional hypermethylation in cancer • Increasing association of chromatin modifying proteins (such as INHAT) to promoters of growth suppressing genes. • Selective advantage • Recruitment of DNMTs- inaccessibility to demethylase • Regional hypermethylation Global hypomethylation is a hallmark of cancer • Repetitive, satellite, centromeric and pericentromeric sequences are hypomethylated in cancer. • Agents that inhibit DNA methyltransferase such as 5-aza-CdR stimulate tumor invasion and metastasis. • Agents that stimulate DNA methylation such as SAM protect from tumorigenesis. • Is there a role for MBD2/demethylase in cancer and metastasis? Inhibition of MBD2/demethylase mRNA by an antisense adenoviral vector dMTase 18 rRNA control GFP dMTase anti DNA methylation is a reversible reaction, chromatin structure defines the direction of the reaction • Chromatin modifying proteins cause regional hypermethylation preventing access to demethylase • Increased MBD2/demethylase is responsible for global hypomethylation and maintaining tumor invasion genes hypomethylated and active • Inhibition of MBD2/demethylase causes hypermethylation and silencing of tumor invasion promoting genes. • MBD2/demethylase is not required for normal cell growth. • MBD2/demethylase is a promising anticancer drug target. Nancy Detich Steffan Hamm Nadia Cervoni Johanne Theberge Paul Campbell Veronica Bovenzi Orval Mamer George Just Debu Chakravarti Sang-beom Seo Shafaat Rabbani Pouya Pakneshan Yongjing Guo