* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chem 3.5 #3 Alcohols 1
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
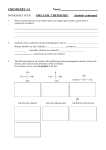
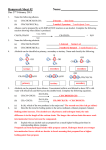
CHEMISTRY 3.5 Name: WORKSHEET THREE 1. 2. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Alkenes & Alcohols Name the following alkenes. (a) CH3CHCHCH2CH2CH3 (b) CH3CH2CHC(CH3)2 Alkenes can be prepared by an ELIMINATION reaction on an alcohol. Complete the following reaction showing what alkene is produced and write the missing reactant over the arrow. CH3CH2CH2OH 3. + H2O Alkenes will react with acidified potassium permanganate. In the reaction the alkene molecule is broken apart at the double bond and the two remnants oxidised up to ketones or carboxylic acids. The following example is done for you. Name the two products. H+/MnO4- CH3CHC(CH3)2 4. 5. CH3COOH + (CH3)2CO Name the following alcohols. (a) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (b) CH3CHOHCH(CH3)2 Alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary. Name and classify the following. CH3 H OH CH3 C OH CH3 C OH CH3CH2 CH3 CH CH3 CH3 OH CH3CH2 CH2 CH2OH 6. CH3CH2C (CH3)2OH CH3CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 Alcohols can be prepared from alkenes. Concentrated sulfuric acid diluted to about 50% with water will effectively add H2O across the double bond. Complete the following equations. Dil. H2SO4 (a) CH3CH=CHCH3 (b) CH2=CHCH3 (c) In (b), which of the two products is the major one? Dil. H2SO4 + 7. 8. 9. (a) Describe the trend in boiling points in the series methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol. (b) Explain why an alcohol such as propanol has a much higher boiling point than its corresponding alkane, propane. (c) Explain why the lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water while the higher ones are not. Alcohols undergo some substitution reactions. The most common ones involve replacement of the OH group with a halogen atom forming haloalkanes. Complete the following equations. (a) CH3CH2CH2OH(l) + PCl5 (s) → (b) What other Phosphorus compound will produce the same reaction as (a)? (c) CH3CH2OH(l) + SOCl2 (l) → (d) The by-products of reaction (c) are both gaseous. Explain how is this an advantage. + POCl3(l) + + + One of the reagents used to make haloalkanes from alcohols can also be used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. This reagent is a mixture of zinc chloride and concentrated hydrochloric acid and is called Lucas reagent. (a) The zinc chloride acts as a (b) Write the equation of the reaction between propan-2-ol and Lucas reagent. (c) Describe the order of the reaction rate between Lucas reagent and primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.