ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4th ed Solution Manual
... t is our hope that in writing this Study Guide and Solutions Manual we will make the study of organic chemistry more meaningful and worthwhile. To be effective, a study guide should be more than just an answer book. What we present here was designed with that larger goal in mind. The Study Guide and ...
... t is our hope that in writing this Study Guide and Solutions Manual we will make the study of organic chemistry more meaningful and worthwhile. To be effective, a study guide should be more than just an answer book. What we present here was designed with that larger goal in mind. The Study Guide and ...
Study Guide and Solutions Manual
... t is our hope that in writing this Study Guide and Solutions Manual we will make the study of organic chemistry more meaningful and worthwhile. To be effective, a study guide should be more than just an answer book. What we present here was designed with that larger goal in mind. The Study Guide and ...
... t is our hope that in writing this Study Guide and Solutions Manual we will make the study of organic chemistry more meaningful and worthwhile. To be effective, a study guide should be more than just an answer book. What we present here was designed with that larger goal in mind. The Study Guide and ...
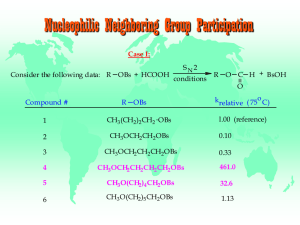
Nucleophilic Neighboring Group Participation Case I
... pathway, one alkene enantiomer will still be produced in excess, and there will be residual optical activity in the product. ...
... pathway, one alkene enantiomer will still be produced in excess, and there will be residual optical activity in the product. ...
Organic Chemistry - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... The carbon shown has 12 electrons around it, 4 more than are allowed. There are 20 valence electrons shown, whereas there should only be 16 (6 from each oxygen and 4 from the carbon). There is nothing wrong with this formula, but it does place a formal charge of –1 on the “left” oxygen and +1 on the ...
... The carbon shown has 12 electrons around it, 4 more than are allowed. There are 20 valence electrons shown, whereas there should only be 16 (6 from each oxygen and 4 from the carbon). There is nothing wrong with this formula, but it does place a formal charge of –1 on the “left” oxygen and +1 on the ...
Infrared - ResearchGate
... the product of a reaction as a known compound. (require access to a file of standard spectra) • At another extreme , different bands observed can be used to deduce the symmetry of the molecule and force constants corresponding to vibrations. • At intermediate levels, deductions may be drawn about th ...
... the product of a reaction as a known compound. (require access to a file of standard spectra) • At another extreme , different bands observed can be used to deduce the symmetry of the molecule and force constants corresponding to vibrations. • At intermediate levels, deductions may be drawn about th ...
Sample
... HBr to alkenes in 1869. Markovnikov stated : MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's ...
... HBr to alkenes in 1869. Markovnikov stated : MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's ...
Lecture 8
... • While glycals were originally used in the synthesis of 2deoxyglycosides, Danishefsky and coworkers devised a glycal strategy that afforded 2-hydroxyglycosides. • Glycals are initially treated with dimethyldioxirane which transfers an oxygen bond to the glycal resulting in an epoxide. • The epox ...
... • While glycals were originally used in the synthesis of 2deoxyglycosides, Danishefsky and coworkers devised a glycal strategy that afforded 2-hydroxyglycosides. • Glycals are initially treated with dimethyldioxirane which transfers an oxygen bond to the glycal resulting in an epoxide. • The epox ...
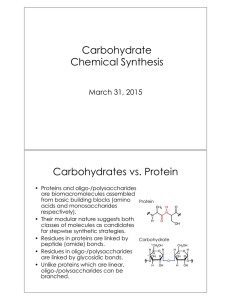
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones
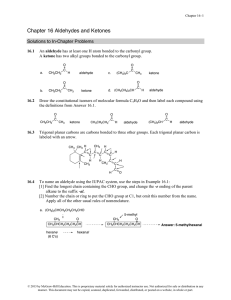
... 16.14 Draw the product of each reaction using Example 16.4 as a guide. Only aldehydes (RCHO) react with Tollens reagent, and they are oxidized to RCO2H. Ketones and alcohols are inert to ...
... 16.14 Draw the product of each reaction using Example 16.4 as a guide. Only aldehydes (RCHO) react with Tollens reagent, and they are oxidized to RCO2H. Ketones and alcohols are inert to ...
Alkenes 4 - ChemWeb (UCC)
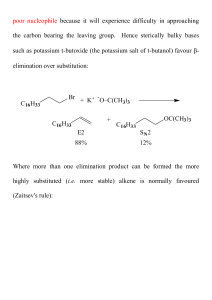
... Alkene formation may also proceed by an E1 (elimination, unimolecular) mechanism which bears the same relationship to E2 that ...
... Alkene formation may also proceed by an E1 (elimination, unimolecular) mechanism which bears the same relationship to E2 that ...
an introduction to organic reactions
... Aldehydes and Ketones I: Nucleophilic Additions to the Carbonyl Group. Aldehydes and Ketones II: Aldol Reactions. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution at the Acyl ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones I: Nucleophilic Additions to the Carbonyl Group. Aldehydes and Ketones II: Aldol Reactions. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Substitution at the Acyl ...
irm_ch15
... them can be used as the ending of the name. The functional groups in this problem, ranked in order of decreasing priority, are: aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, and alkoxy. a. The compound has two functional groups, a ketone and an alcohol; the ketone has priority, so this compound is named as a ketone. b ...
... them can be used as the ending of the name. The functional groups in this problem, ranked in order of decreasing priority, are: aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, and alkoxy. a. The compound has two functional groups, a ketone and an alcohol; the ketone has priority, so this compound is named as a ketone. b ...
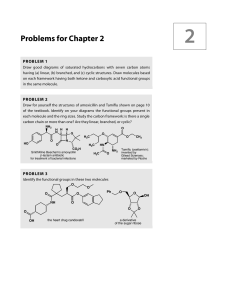
Problems for Chapter 2
... PROB LE M 7 Four compounds having the formula C4H6O2 have the IR and NMR data given below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) ...
... PROB LE M 7 Four compounds having the formula C4H6O2 have the IR and NMR data given below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) ...
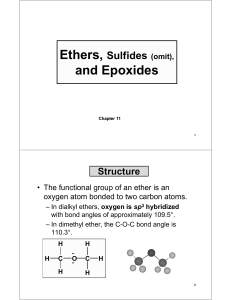
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... 9.5B Interesting Ethers The discovery that diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) is a general anesthetic revolutionized surgery in the nineteenth century. For years, a heated controversy existed over who first discovered diethyl ether’s anesthetic properties and recognized the enormous benefit in its use. E ...
... 9.5B Interesting Ethers The discovery that diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) is a general anesthetic revolutionized surgery in the nineteenth century. For years, a heated controversy existed over who first discovered diethyl ether’s anesthetic properties and recognized the enormous benefit in its use. E ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... a. Add 1-pentene to water (Markovnikov Addition) and 2-pentanol will be prepared in a 100% yield ...
... a. Add 1-pentene to water (Markovnikov Addition) and 2-pentanol will be prepared in a 100% yield ...
Course Notes
... Nuclei of bonded atoms undergo vibrations similar to two balls connected by a spring. Depending on the particular atoms bonded to each other (and their masses) the frequency of this vibration will vary. Infrared energy is absorbed by molecules resulting in an excited vibrational state. Vibrations oc ...
... Nuclei of bonded atoms undergo vibrations similar to two balls connected by a spring. Depending on the particular atoms bonded to each other (and their masses) the frequency of this vibration will vary. Infrared energy is absorbed by molecules resulting in an excited vibrational state. Vibrations oc ...
Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas
... derivatization of some drugs [84,85]. N-Methylbis(trifluoroacetamide) (MBTFA) is very volatile and by-product N-methyltrifluoroacetamide does not cause column damage. MBTFA can be useful for N-selective acylation after trimethylsilylation of hydroxyamino compounds [86]. Among these acylating reagent ...
... derivatization of some drugs [84,85]. N-Methylbis(trifluoroacetamide) (MBTFA) is very volatile and by-product N-methyltrifluoroacetamide does not cause column damage. MBTFA can be useful for N-selective acylation after trimethylsilylation of hydroxyamino compounds [86]. Among these acylating reagent ...
Chapter 6 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
... CH3 H OH group is attached to the less substituted carbon. ...
... CH3 H OH group is attached to the less substituted carbon. ...
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
- Article One Partners
... channel-antagonistic and anticonvulsive properties. They are prepared by a relatively expensive method generating enantiomer mixtures which may be split into the individual optical antipodes. The present invention is aimed at preparing and employing compounds which can be chemically generated by sim ...
... channel-antagonistic and anticonvulsive properties. They are prepared by a relatively expensive method generating enantiomer mixtures which may be split into the individual optical antipodes. The present invention is aimed at preparing and employing compounds which can be chemically generated by sim ...
barker_rg
... factor besides disproportionation which makes their preparation and purification The presence of moisture in solvents or as water vapor ...
... factor besides disproportionation which makes their preparation and purification The presence of moisture in solvents or as water vapor ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.