as a PDF
... metals. It attempts to fill a slot between the general text and the in-depth review or monograph. The organometallic chemistry is confined to cr-bonded compounds in normal oxidation states; compounds with 7r-bonding ligands are generally excluded. Their inclusion would have increased the length of t ...
... metals. It attempts to fill a slot between the general text and the in-depth review or monograph. The organometallic chemistry is confined to cr-bonded compounds in normal oxidation states; compounds with 7r-bonding ligands are generally excluded. Their inclusion would have increased the length of t ...
4134gdisk doc..4134gdisk chapter .. Page501
... There has been a theoretical study of the mechanism of proton-coupled electrontransfer reactions74 and a study of proton-coupled electron-transfer from sulfur.75 The combination of stopped flow technology and EXAFS has allowed the investigation of the structure of short-lived intermediates in some r ...
... There has been a theoretical study of the mechanism of proton-coupled electrontransfer reactions74 and a study of proton-coupled electron-transfer from sulfur.75 The combination of stopped flow technology and EXAFS has allowed the investigation of the structure of short-lived intermediates in some r ...
Late Transition Metal Amido Complexes: Electronic
... atom.[2b] This development has led to a broad variety of early transition metal complexes with unprecedented reactivity patterns. In contrast, electron rich late transition complexes in low oxidation states (d6 - d10) with amido ligands were until more recently comparatively rare.[3] Their participa ...
... atom.[2b] This development has led to a broad variety of early transition metal complexes with unprecedented reactivity patterns. In contrast, electron rich late transition complexes in low oxidation states (d6 - d10) with amido ligands were until more recently comparatively rare.[3] Their participa ...
an introduction to organic reactions
... saying that Organic Chemistry really isn't that bad and can, in fact, be pretty interesting. I think it's important to understand from the start that this is completely true…I can almost assure you that you will enjoy Orgo much more than General Chemistry, and the work & endash; although there may b ...
... saying that Organic Chemistry really isn't that bad and can, in fact, be pretty interesting. I think it's important to understand from the start that this is completely true…I can almost assure you that you will enjoy Orgo much more than General Chemistry, and the work & endash; although there may b ...
OC 2/e Ch 11
... • the OH group, however, is more acidic (pKa 16-18) than the terminal alkyne (pKa 25) • treating the compound with one mole of NaNH2 will give the alkoxide anion rather than the acetylide HC CCH2 CH2 CH 2 OH + N a+ NH 2 4-Pentyn-1-ol HC CCH2 CH2 CH 2 O- Na + + N H3 ...
... • the OH group, however, is more acidic (pKa 16-18) than the terminal alkyne (pKa 25) • treating the compound with one mole of NaNH2 will give the alkoxide anion rather than the acetylide HC CCH2 CH2 CH 2 OH + N a+ NH 2 4-Pentyn-1-ol HC CCH2 CH2 CH 2 O- Na + + N H3 ...
Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas
... detection (CLD) [43,52] and GC-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [41,46] have been investigated. By using these methods, sub-nanogram detection limits have been achieved. However, the GC of free amines generally has some inherent problems related to the difficulty in handling low-molecular-mass amines becau ...
... detection (CLD) [43,52] and GC-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [41,46] have been investigated. By using these methods, sub-nanogram detection limits have been achieved. However, the GC of free amines generally has some inherent problems related to the difficulty in handling low-molecular-mass amines becau ...
b - Gordon State College
... 2) Find the moles of each reactant: moles = mass in gram / molar mass 3) Pick up any reactant, say A, and use the stoichiometry to calculate the required amount of the other reactant B. 4) Compare the required amount of B with the available amount of B. a) If required > available, then B is the limi ...
... 2) Find the moles of each reactant: moles = mass in gram / molar mass 3) Pick up any reactant, say A, and use the stoichiometry to calculate the required amount of the other reactant B. 4) Compare the required amount of B with the available amount of B. a) If required > available, then B is the limi ...
Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic
... and nonelectrochemical approaches are closer in relative merit. An experimental protocol making use of the complementary aspects of both approaches is often more effective than either individual method. Controlled potential electrolysis (CPE) is the electrochemical method most often adopted for synt ...
... and nonelectrochemical approaches are closer in relative merit. An experimental protocol making use of the complementary aspects of both approaches is often more effective than either individual method. Controlled potential electrolysis (CPE) is the electrochemical method most often adopted for synt ...
One-pot aqueous synthesis of cysteine-capped
... 2004; Kuno et al. 2006). These methods generally require the use of organic solvents, high temperature or pressure, oxygen and water-free conditions, and toxic reagents, such as three octyl phosphine (TOP three) and trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO), all of which increase operational difficulty and pre ...
... 2004; Kuno et al. 2006). These methods generally require the use of organic solvents, high temperature or pressure, oxygen and water-free conditions, and toxic reagents, such as three octyl phosphine (TOP three) and trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO), all of which increase operational difficulty and pre ...
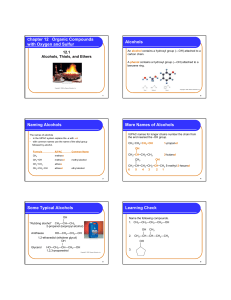
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
... • contains an –O– between two carbon groups • has a common name that gives the alkyl names of the attached groups, followed by ether ...
... • contains an –O– between two carbon groups • has a common name that gives the alkyl names of the attached groups, followed by ether ...
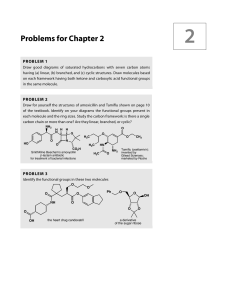
Problems for Chapter 2
... PROB LE M 7 Four compounds having the formula C4H6O2 have the IR and NMR data given below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) ...
... PROB LE M 7 Four compounds having the formula C4H6O2 have the IR and NMR data given below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) ...
REVIEWS Environmental remediation by photocatalysis R. Vinu AND Giridhar Madras
... and mechanism of photocatalysis,8–23 with special emphasis on the electron transfer processes, lattice and electronic structure of TiO2 , surface chemistry of semiconductor oxides, generation of reactive radicals, chemisorption of small and large molecules, surface modification by doping, photooxidat ...
... and mechanism of photocatalysis,8–23 with special emphasis on the electron transfer processes, lattice and electronic structure of TiO2 , surface chemistry of semiconductor oxides, generation of reactive radicals, chemisorption of small and large molecules, surface modification by doping, photooxidat ...
Document
... • IUPAC name: We replace the -e in alkane name with -ol. • Common name: As simple alcohols using the name of the alkyl group followed by “alcohol”. ...
... • IUPAC name: We replace the -e in alkane name with -ol. • Common name: As simple alcohols using the name of the alkyl group followed by “alcohol”. ...
Document
... • Clean elimination takes place because the reaction mixture contains no good nucleophile to react with the intermediate carbocation, so no competing SN1 reaction occurs. • This makes the E1 dehydration of alcohols much more synthetically useful than the E1 dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. ...
... • Clean elimination takes place because the reaction mixture contains no good nucleophile to react with the intermediate carbocation, so no competing SN1 reaction occurs. • This makes the E1 dehydration of alcohols much more synthetically useful than the E1 dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
The Impact of Ligand Design on the Coordination Chemistry and
... [XZY] where Z is the central, anchoring Lewis donor while X and Y are flanking Lewis donors. Ever since initial reports of transition metal pincer complexes were published in the late 1970’s, there has been burgeoning interest in such complexes because of their desirable robust nature, generally sim ...
... [XZY] where Z is the central, anchoring Lewis donor while X and Y are flanking Lewis donors. Ever since initial reports of transition metal pincer complexes were published in the late 1970’s, there has been burgeoning interest in such complexes because of their desirable robust nature, generally sim ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.