Lecture8
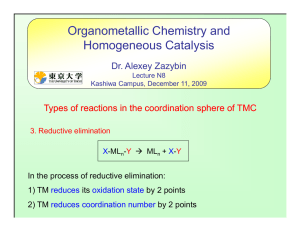
... Direct nucleophilic addition to an unsaturated ligand (e.g. CO, alkene, allyl, benzene) Because they are electron rich, molecules such as CO, alkenes, polyenes and arenes generally do not react with nucleophiles in the absence of a metal. • Once attached to a metal, these ligands give up some of th ...
... Direct nucleophilic addition to an unsaturated ligand (e.g. CO, alkene, allyl, benzene) Because they are electron rich, molecules such as CO, alkenes, polyenes and arenes generally do not react with nucleophiles in the absence of a metal. • Once attached to a metal, these ligands give up some of th ...
Chapter 4 Metal nanoparticles stabilized by chiral ligands with carbohydrate backbone
... molecular species. Diphosphite chiral ligands were also used as stabilisers of palladium nanoparticles.[79] These palladium nanoparticles were active in the ...
... molecular species. Diphosphite chiral ligands were also used as stabilisers of palladium nanoparticles.[79] These palladium nanoparticles were active in the ...
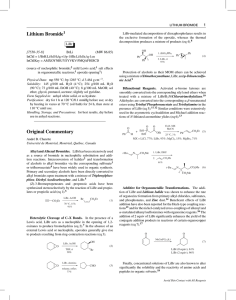
Lithium Bromide Original Commentary
... acid in a variety of reactions. For example, this reagent was used in the Pictet-Spengler cyclization of a highly functionalized imine (eq 13).33 In this reaction, carbon-carbon bond formation occurs without reaction or loss of stereochemical integrity of the α-amino nitrile functionality. Lithium b ...
... acid in a variety of reactions. For example, this reagent was used in the Pictet-Spengler cyclization of a highly functionalized imine (eq 13).33 In this reaction, carbon-carbon bond formation occurs without reaction or loss of stereochemical integrity of the α-amino nitrile functionality. Lithium b ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • NaBH4 is less reactive and hence more selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
... • NaBH4 is less reactive and hence more selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... and compounds related to them. These are ionic reactions in which one group on the molecule (a leaving group) is replaced by another group (a nucleophile). The transformation of haloalkanes (R-X) into alcohols (R-OH) where an OH group replaces the halogen (X) is an example of nucleophilic substituti ...
... and compounds related to them. These are ionic reactions in which one group on the molecule (a leaving group) is replaced by another group (a nucleophile). The transformation of haloalkanes (R-X) into alcohols (R-OH) where an OH group replaces the halogen (X) is an example of nucleophilic substituti ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
... reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depend ...
... reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depend ...
CYPRUS
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
organic practice problems
... ____ 60. Which of the following molecules is ethanol? a. C2H6 b. CH3CO2H c. CH3CHO d. CH3CH2OH e. CH3OCH3 ____ 61. Which functional group does not contain an oxygen atom? a. alcohol b. amine c. amide d. ester e. ether ____ 62. The functional group RCO2R' is characteristic of an ________. a. ether b. ...
... ____ 60. Which of the following molecules is ethanol? a. C2H6 b. CH3CO2H c. CH3CHO d. CH3CH2OH e. CH3OCH3 ____ 61. Which functional group does not contain an oxygen atom? a. alcohol b. amine c. amide d. ester e. ether ____ 62. The functional group RCO2R' is characteristic of an ________. a. ether b. ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determining step is the ionization step (the first step) that involves only the haloalkane substrate (RX). The E1 r ...
... This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determining step is the ionization step (the first step) that involves only the haloalkane substrate (RX). The E1 r ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES I. NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO …
... •Once the substrate (aldehyde or ketone) is bound to the enzyme, the active site of the enzyme is in a position to react with and modify the substrate. •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from ...
... •Once the substrate (aldehyde or ketone) is bound to the enzyme, the active site of the enzyme is in a position to react with and modify the substrate. •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from ...
High-Oxidation-State Palladium Catalysis: New Reactivity for
... the presence of strong oxidants, which prevent further palladium(II)promoted reactions at a given point of the catalytic cycle by selective metal oxidation. The resulting higher-oxidation-state palladium complexes have been used to develop a series of new synthetic transformations that cannnot be re ...
... the presence of strong oxidants, which prevent further palladium(II)promoted reactions at a given point of the catalytic cycle by selective metal oxidation. The resulting higher-oxidation-state palladium complexes have been used to develop a series of new synthetic transformations that cannnot be re ...
Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
... This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determining step is the ionization step (the first step) that involves only the haloalkane substrate (RX). The E1 r ...
... This E1 mechanism is analogous to the two-step SN1 substitution mechanism (Chapter 7). The "1" in E1 indicates that the rate determining step of the reaction is unimolecular. This rate determining step is the ionization step (the first step) that involves only the haloalkane substrate (RX). The E1 r ...
Oxidative Alihatic Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage Reactions
... biomass for fuel production, applications in wastewater treatment and bioremediation, and in developing new reactions for organic synthesis of fine chemicals including pharmaceuticals. Ideally these reactions would be carried out with high atom economy at low temperatures and pressures, and using ea ...
... biomass for fuel production, applications in wastewater treatment and bioremediation, and in developing new reactions for organic synthesis of fine chemicals including pharmaceuticals. Ideally these reactions would be carried out with high atom economy at low temperatures and pressures, and using ea ...
Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
... Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
Document
... cf. stereoselective • When a mixture of stereoisomers is possible from a dehydrohalogenation, the major product is the more stable stereoisomer. • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselec ...
... cf. stereoselective • When a mixture of stereoisomers is possible from a dehydrohalogenation, the major product is the more stable stereoisomer. • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselec ...
Alcools
... The OH group has a higher priority than a multiple CC bond, a halogen, and an alkyl group in determining the carbon chain numbering. ...
... The OH group has a higher priority than a multiple CC bond, a halogen, and an alkyl group in determining the carbon chain numbering. ...
Document
... cf. stereoselective • When a mixture of stereoisomers is possible from a dehydrohalogenation, the major product is the more stable stereoisomer. • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselec ...
... cf. stereoselective • When a mixture of stereoisomers is possible from a dehydrohalogenation, the major product is the more stable stereoisomer. • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselec ...
Enzyme Properties
... the hydroxyl group of the anomeric carbon is replaced via condensation with an alcohol, an amine, or a thiol All oligosaccharides are glycosides, but so are a lot of monomeric sugar ...
... the hydroxyl group of the anomeric carbon is replaced via condensation with an alcohol, an amine, or a thiol All oligosaccharides are glycosides, but so are a lot of monomeric sugar ...
Synthetic Organic Chemistry - Name
... Fig.1 Structure of (LiC2H5)4 with tetrahedral geometry NMR studies also indicate that methyl lithium retains the tetrameric solid state structure in solution. The structures of (Li-R)4 units i.e tetrameric depicted by X2 ...
... Fig.1 Structure of (LiC2H5)4 with tetrahedral geometry NMR studies also indicate that methyl lithium retains the tetrameric solid state structure in solution. The structures of (Li-R)4 units i.e tetrameric depicted by X2 ...
B.Sc Chemistry - Calicut University
... 2. Chemistry in everyday life 3. Plastics and rubbers in everyday life In the sixth semester there are five elective courses. An institution can chose any one of ...
... 2. Chemistry in everyday life 3. Plastics and rubbers in everyday life In the sixth semester there are five elective courses. An institution can chose any one of ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.