Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones
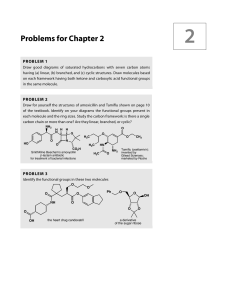
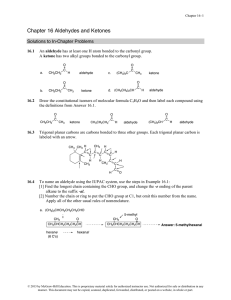
... An aldehyde cannot have the molecular formula C5H12O. C5H12 has too many H’s. Since an aldehyde has a double bond, the number of C’s and H’s resembles an alkene, not an alkane. An aldehyde with 5 C’s would have the molecular formula C5H10O. ...
... An aldehyde cannot have the molecular formula C5H12O. C5H12 has too many H’s. Since an aldehyde has a double bond, the number of C’s and H’s resembles an alkene, not an alkane. An aldehyde with 5 C’s would have the molecular formula C5H10O. ...
Alkenes 4 - ChemWeb (UCC)
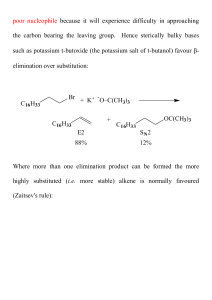
... poor nucleophile because it will experience difficulty in approaching the carbon bearing the leaving group. Hence sterically bulky bases such as potassium t-butoxide (the potassium salt of t-butanol) favour elimination over substitution: ...
... poor nucleophile because it will experience difficulty in approaching the carbon bearing the leaving group. Hence sterically bulky bases such as potassium t-butoxide (the potassium salt of t-butanol) favour elimination over substitution: ...
irm_ch15
... molecules raise the boiling point. Alkanes are nonpolar, and so do not have these attractive forces holding them together. 15.40 Dipole-dipole interactions present for aldehydes and ketones are weaker than the hydrogen bonds present for alcohols. 15.41 The number of hydrogen bonds that can form betw ...
... molecules raise the boiling point. Alkanes are nonpolar, and so do not have these attractive forces holding them together. 15.40 Dipole-dipole interactions present for aldehydes and ketones are weaker than the hydrogen bonds present for alcohols. 15.41 The number of hydrogen bonds that can form betw ...
OC 2/e 9 Alcohols
... ethanol are about as accessible as hydroxide ion for solvation; these alcohol are about as acidic as water. • as the bulk of the alkyl group increases, the ability of water to solvate the alkoxide decreases, the acidity of the alcohol decreases, and the basicity of the alkoxide ion increases. ...
... ethanol are about as accessible as hydroxide ion for solvation; these alcohol are about as acidic as water. • as the bulk of the alkyl group increases, the ability of water to solvate the alkoxide decreases, the acidity of the alcohol decreases, and the basicity of the alkoxide ion increases. ...
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur Alcohols
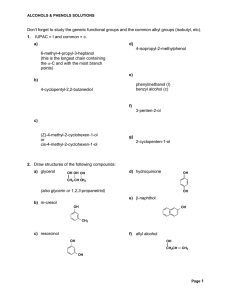
... 1. CH3─CH2─ CH2─CH2─CH2─CH2─OH No; an alcohol with a long carbon chain (nonpolar) is not soluble. 2. CH3─O─CH2─CH3 Yes; an O atom can hydrogen bond with water. 3. CH3─CH2─CH2─OH Yes; short-chain alcohols hydrogen bond with water. ...
... 1. CH3─CH2─ CH2─CH2─CH2─CH2─OH No; an alcohol with a long carbon chain (nonpolar) is not soluble. 2. CH3─O─CH2─CH3 Yes; an O atom can hydrogen bond with water. 3. CH3─CH2─CH2─OH Yes; short-chain alcohols hydrogen bond with water. ...
Sample
... MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's rule. Reactions that follow this rule are sai ...
... MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's rule. Reactions that follow this rule are sai ...
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... The bond angle around the O atom in an alcohol or ether is similar to the tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°. In contrast, the C – O – C bond angle of an epoxide must be 60°, a considerable deviation from the tetrahedral bond angle. For this reason, epoxides have angle strain, making them much more re ...
... The bond angle around the O atom in an alcohol or ether is similar to the tetrahedral bond angle of 109.5°. In contrast, the C – O – C bond angle of an epoxide must be 60°, a considerable deviation from the tetrahedral bond angle. For this reason, epoxides have angle strain, making them much more re ...
Compounds with Oxygen Atoms
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
Alcohol, Ethers, and Thiols
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
Alcohols, Phenols, Thiols, & Ethers
... Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were ...
... Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were ...
CH 2
... Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were ...
... Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were ...
Chapter 1.4 Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
... • like diethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • developed by the 1960’s were nonflammable. ...
SUPPORTED LIGANDS FOR METAL CATALYZED REACTIONS Rocío Marcos Escartín ISBN:
... ISBN: Dipòsit Legal: T.1217-2011 ...
... ISBN: Dipòsit Legal: T.1217-2011 ...
Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols
... • Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • Developed by 1960s were nonflammable. ...
... • Such as ethyl ether CH3─CH2─O─CH2─CH3 were used for over a century, but caused nausea and were flammable. • Developed by 1960s were nonflammable. ...
YEAR 1
... electron-pushing mechanisms, electron delocalization, molecular orbital theory and modern instrumental techniques. Laboratory experiences include chemical separations, examination of reaction selectivity, and isolation of natural products. Prerequisites: Chem 1270 and Chem 1280 or Chem 1370 and Chem ...
... electron-pushing mechanisms, electron delocalization, molecular orbital theory and modern instrumental techniques. Laboratory experiences include chemical separations, examination of reaction selectivity, and isolation of natural products. Prerequisites: Chem 1270 and Chem 1280 or Chem 1370 and Chem ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... 1. Oxidation – Tollens Test - Benedicts Test 2. Reduction – Hydrogen addition – NaBH4 reagent 3. Addition of Alcohols – hemiacetal/acetal and tautomerism ...
... 1. Oxidation – Tollens Test - Benedicts Test 2. Reduction – Hydrogen addition – NaBH4 reagent 3. Addition of Alcohols – hemiacetal/acetal and tautomerism ...
Elimination Reactions
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
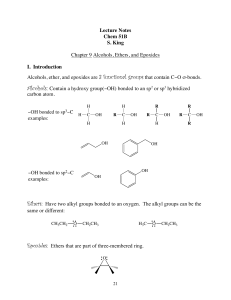
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and
... An ether is prepared by treating an alkoxide with an alkyl halide. This is known as a Williamson ether synthesis. CH3 ...
... An ether is prepared by treating an alkoxide with an alkyl halide. This is known as a Williamson ether synthesis. CH3 ...
Lecture 8
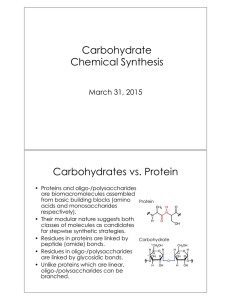
... • While glycals were originally used in the synthesis of 2deoxyglycosides, Danishefsky and coworkers devised a glycal strategy that afforded 2-hydroxyglycosides. • Glycals are initially treated with dimethyldioxirane which transfers an oxygen bond to the glycal resulting in an epoxide. • The epox ...
... • While glycals were originally used in the synthesis of 2deoxyglycosides, Danishefsky and coworkers devised a glycal strategy that afforded 2-hydroxyglycosides. • Glycals are initially treated with dimethyldioxirane which transfers an oxygen bond to the glycal resulting in an epoxide. • The epox ...
Department of Chemistry
... majors. Students cannot receive credit for both CHEM 206 and CHEM 215–216. Prerequisite: CHEM 201. Occasionally. CHEM 207 Survey of Organic Chemistry and Petrochemicals 4.0; 4 cr. A survey of organic chemistry which covers mainly spectroscopy, multi-step synthesis, properties and reactions of al ...
... majors. Students cannot receive credit for both CHEM 206 and CHEM 215–216. Prerequisite: CHEM 201. Occasionally. CHEM 207 Survey of Organic Chemistry and Petrochemicals 4.0; 4 cr. A survey of organic chemistry which covers mainly spectroscopy, multi-step synthesis, properties and reactions of al ...
Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... in research and teaching, and according to Essential Science Indicators, he is currently ranked as the Top 1% most cited Chemists worldwide. He has published four books and over 80 scientific papers in top international journals such as J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem., Org. Lett., and J. Org. Chem. ...
... in research and teaching, and according to Essential Science Indicators, he is currently ranked as the Top 1% most cited Chemists worldwide. He has published four books and over 80 scientific papers in top international journals such as J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem., Org. Lett., and J. Org. Chem. ...
Organic Chemistry
... in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride or methyl shift to form a more stable carbocation) might occur, typical of reactions that have a carbocation intermediat ...
... in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride or methyl shift to form a more stable carbocation) might occur, typical of reactions that have a carbocation intermediat ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.