Silylation Overview - Sigma
... The term “silylation” is defined as the substitution of a hydrogen atom bound to a hetero atom (– OH, = NH, – SH) by a silyl group, forming a silicon hetero atom bond, without any further alteration of the molecule. Excluded from this review are therefore the silylation of carbon atoms, hydrosilylat ...
... The term “silylation” is defined as the substitution of a hydrogen atom bound to a hetero atom (– OH, = NH, – SH) by a silyl group, forming a silicon hetero atom bond, without any further alteration of the molecule. Excluded from this review are therefore the silylation of carbon atoms, hydrosilylat ...
Department of Chemistry
... General Chemistry II 3.0; 3 cr. A course that covers solutions, chemical equilibrium, kinetics, acid-base and solubility equilibria, introductory thermodynamics and electrochemistry; surveys common groups in the periodic table; provides an introduction to organic chemistry and nuclear chemistry. P ...
... General Chemistry II 3.0; 3 cr. A course that covers solutions, chemical equilibrium, kinetics, acid-base and solubility equilibria, introductory thermodynamics and electrochemistry; surveys common groups in the periodic table; provides an introduction to organic chemistry and nuclear chemistry. P ...
ch12 - Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
... • is highly toxic and found in windshield washer fluid, Sterno, and paint strippers • is rapidly absorbed and oxidized to formaldehyde and then ...
... • is highly toxic and found in windshield washer fluid, Sterno, and paint strippers • is rapidly absorbed and oxidized to formaldehyde and then ...
Department of Chemistry
... A brief survey designed for students majoring in agriculture or public health that covers the following topics: hydrocarbons, stereoisomerism, organo halogens, oxygen containing groups, carbonyl groups, carboxylic acids and their derivatives, amines, carbohydrates, and amino-acids. Students cannot r ...
... A brief survey designed for students majoring in agriculture or public health that covers the following topics: hydrocarbons, stereoisomerism, organo halogens, oxygen containing groups, carbonyl groups, carboxylic acids and their derivatives, amines, carbohydrates, and amino-acids. Students cannot r ...
14A
... bonded to it bears a partial positive charge – however, only weak forces of attraction exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid – consequently, boiling points of ethers are close to those of hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight – ethers have lower boiling points than alcohols of the same ...
... bonded to it bears a partial positive charge – however, only weak forces of attraction exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid – consequently, boiling points of ethers are close to those of hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight – ethers have lower boiling points than alcohols of the same ...
Project Overview
... These PowerPoint Lecture Slides were created and prepared by Professor William Tam and his wife, Dr. Phillis Chang. Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the ...
... These PowerPoint Lecture Slides were created and prepared by Professor William Tam and his wife, Dr. Phillis Chang. Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
... 44) As the molar mass of these alcohols increases, the water solubility decreases. This occurs because the polarity of the hydroxyl group, which is the reason for the interaction with the polar water molecules, becomes less important as the size of the nonpolar hydrocarbon portion of the molecule in ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
Alcohols phenols
... By hydrolysis of alkyl halides. Alkyl halides on hydrolysis with aqueous alkalies or moist silver oxide give alcohols. In general, alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols as the latter are easily available. It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which hydroxide ion substitutes halide ions. A ...
... By hydrolysis of alkyl halides. Alkyl halides on hydrolysis with aqueous alkalies or moist silver oxide give alcohols. In general, alkyl halides are prepared from alcohols as the latter are easily available. It is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which hydroxide ion substitutes halide ions. A ...
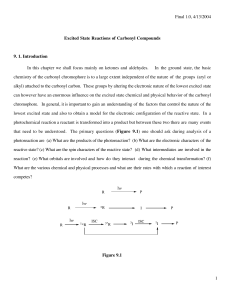
Excited State Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
... Reduction in the ground state is one of the most useful reactions of carbonyl chromophore. A number of reagents have been developed to selectively reduce carbonyl chromophores present as a part of various functional groups (ester vs. ketone etc.). However, one can‘t selectively reduce in the ground ...
... Reduction in the ground state is one of the most useful reactions of carbonyl chromophore. A number of reagents have been developed to selectively reduce carbonyl chromophores present as a part of various functional groups (ester vs. ketone etc.). However, one can‘t selectively reduce in the ground ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
Alkyl Halides SN and E reactions
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
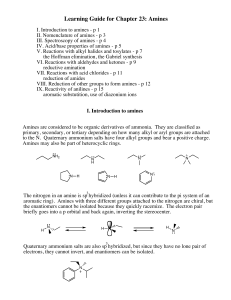
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
... VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified ...
... VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified ...
Topic 22 Notes
... 2. Single and multiple covalent bonds a. Single covalent bonds (1) Where one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms. (2) Symbolized by one pair of dots or by a dash. b. Double covalent bonds (1) Where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. (2) Symbolized by two pairs of dots or ...
... 2. Single and multiple covalent bonds a. Single covalent bonds (1) Where one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms. (2) Symbolized by one pair of dots or by a dash. b. Double covalent bonds (1) Where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. (2) Symbolized by two pairs of dots or ...
Reactions
... H2O H2SO4 The regiochemistry is determined by the relative stability of the intermediate carbocation. But what if you want 1-propyl alcohol? What could you do to “trick” the regiochemistry? ...
... H2O H2SO4 The regiochemistry is determined by the relative stability of the intermediate carbocation. But what if you want 1-propyl alcohol? What could you do to “trick” the regiochemistry? ...
Camp 1 - TypePad
... Ethers resemble hydrocarbons in their resistance to chemical reaction. • They do not react with oxidizing agents such as potassium dichromate. • They do not react with reducing agents such as H2 in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. • They are not affected by most acids or bases at moderat ...
... Ethers resemble hydrocarbons in their resistance to chemical reaction. • They do not react with oxidizing agents such as potassium dichromate. • They do not react with reducing agents such as H2 in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. • They are not affected by most acids or bases at moderat ...
Handout 3
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
Slide 1
... Cope Elimination: A tertiary amine is converted to the amine oxide by treatment with hydrogen peroxide or a peroxyacid. The amine oxide is then thermally decomposed to give an ...
... Cope Elimination: A tertiary amine is converted to the amine oxide by treatment with hydrogen peroxide or a peroxyacid. The amine oxide is then thermally decomposed to give an ...
Nucleophilic ring opening of aziridines
... The aziridine functionality, or alternatively named the azaethylene or ethylenimine unit, represents one of the most valuable three membered ring systems in modern synthetic chemistry, because of its widely recognized versatility as a significant building block for chemical bond elaborations and fun ...
... The aziridine functionality, or alternatively named the azaethylene or ethylenimine unit, represents one of the most valuable three membered ring systems in modern synthetic chemistry, because of its widely recognized versatility as a significant building block for chemical bond elaborations and fun ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... conformations determined from electron diffraction studies by the Norwegian physical chemist Odd Hassel. Thus conformational analysis, which ever after changed the way organic chemists think about structure, synthesis and chemical reactivity, came into being. Barton and Hassel shared the 1969 Nobel ...
... conformations determined from electron diffraction studies by the Norwegian physical chemist Odd Hassel. Thus conformational analysis, which ever after changed the way organic chemists think about structure, synthesis and chemical reactivity, came into being. Barton and Hassel shared the 1969 Nobel ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.